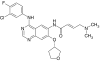
A phase I dose escalation study of BIBW 2992, an irreversible dual inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor 1 (EGFR) and 2 (HER2) tyrosine kinase in a 2-week on, 2-week off schedule in patients with advanced solid tumours
- PMID: 18026190
- PMCID: PMC2359721
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604108
A phase I dose escalation study of BIBW 2992, an irreversible dual inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor 1 (EGFR) and 2 (HER2) tyrosine kinase in a 2-week on, 2-week off schedule in patients with advanced solid tumours
Abstract
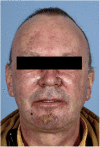
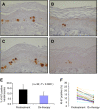
To assess tolerability, pharmacokinetics (PK), pharmacodynamics (PD) and clinical activity of the dual epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) 1 and 2 (HER2) tyrosine kinase inhibitor BIBW 2992. An escalating schedule of once-daily (OD) BIBW 2992 for 14 days followed by 14 days off medication was explored. Thirty-eight patients were enrolled. Dose levels were 10, 20, 30, 45, 70, 85, and 100 mg. At 100 mg dose-limiting toxicity (DLT) (common toxicity criteria grade 3 skin rash and grade 3 diarrhoea despite treatment with loperamide) occurred in two patients. In the next-lower dose of 70 mg, DLT (grade 3 fatigue and ALAT elevation) occurred in one of six patients. An intermediate dose level of 85 mg was studied. Here DLT occurred in two patients (grade 3 diarrhoea despite treatment and grade 2 diarrhoea lasting more than 7 days despite treatment). An additional 12 patients were treated at 70 mg. BIBW 2992 PK after single and multiple doses revealed moderately fast absorption, and no deviation from dose proportionality. Pharmacodynamics analysis in skin biopsies did not show significant changes in EGFR-associated biomarkers. However, a significant inhibitory effect on the proliferation index of epidermal keratinocytes was observed. No partial or complete responses were observed, stable disease lasting more than four cycles was seen in seven patients. The recommended dose for studies with BIBW 2992 for 14 days followed by 14 days off medication is 70 mg OD.
Figures

References
-
- Agus D, Terlizzi E, Stopfer P, Amelsberg A, Gordon M (2006) A phase I dose escalation study of BIBW 2992, an irreversible dual EGFR/HER2 receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in a continuous schedule in patients with advanced solid tumours. J Clin Oncol 24: 49s (suppl, abstract 2074)
-
- Baselga J, Rischin D, Ranson M, Cavert H, Raymond E, Kieback D, Kaye S, Gianni L, Harris A, Bjork T, Averbuch S, Feyereislova A, Swaisland H, Rojo F, Albanell J (2002) Phase I safety, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic trial of ZD1839, a selective oral epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with five selected solid tumor types. J Clin Oncol 20: 4292–4302 - PubMed
-
- Burris H, Hurwitz H, Dees E, Dowlati A, Blackwell K, O'Neil B, Marcom P, Ellis M, Overmoyer B, Jones S, Harris J, Smith D, Koch K, Stead A, Mangum S, Spector N (2005) Phase I safety, pharmacokinetics, and clinical activity study of lapatinib (GW572016), a reversible dual inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases, in heavily pretreated patients with metastatic carcinomas. J Clin Oncol 23: 5305–5313 - PubMed
-
- Carter E, Wodicka L, Shah N, Velasco A, Fabian M, Treiber D, Milanov Z, Atteridge C, Biggs W, Edeen P, Floyd M, Ford J, Grotzfeld R, Herrgard S, Insko D, Mehta S, Patel H, Pao W, Sawyers C, Varmus H, Zarrinkar P, Lockhart D (2005) Inhibition of drug-resistant mutants of ABL, KIT, and EGF receptor kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 11011–11016 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dittrich Ch, Greim G, Borner M, Weigang-Köhler K, Huisman H, Amelsberg A, Ehret A, Wanders J, Hanauske A, Fumoleau P (2002) Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of BIBX 1382 BS, an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor, given in a continuous daily oral administration. Eur J Cancer 38: 1072–1080 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

