Targeting selectins and selectin ligands in inflammation and cancer
- PMID: 18028011
- PMCID: PMC2559865
- DOI: 10.1517/14728222.11.11.1473
Targeting selectins and selectin ligands in inflammation and cancer
Abstract
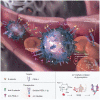
Inflammation and cancer metastasis are associated with extravasation of leukocytes or tumor cells from blood into tissue. Such movement is believed to follow a coordinated and sequential molecular cascade initiated, in part, by the three members of the selectin family of carbohydrate-binding proteins: E-selectin (CD62E), L-selectin (CD62L) and P-selectin (CD62P). E-selectin is particularly noteworthy in disease by virtue of its expression on activated endothelium and on bone-skin microvascular linings and for its role in cell rolling, cell signaling and chemotaxis. E-selectin, along with L- or P-selectin, mediates cell tethering and rolling interactions through the recognition of sialo-fucosylated Lewis carbohydrates expressed on structurally diverse protein-lipid ligands on circulating leukocytes or tumor cells. Major advances in understanding the role of E-selectin in inflammation and cancer have been advanced by experiments assaying E-selectin-mediated rolling of leukocytes and tumor cells under hydrodynamic shear flow, by clinical models of E-selectin-dependent inflammation, by mice deficient in E-selectin and by mice deficient in glycosyltransferases that regulate the binding activity of E-selectin ligands. Here, the authors elaborate on how E-selectin and its ligands may facilitate leukocyte or tumor cell recruitment in inflammatory and metastatic settings. Antagonists that target cellular interactions with E-selectin and other members of the selectin family, including neutralizing monoclonal antibodies, competitive ligand inhibitors or metabolic carbohydrate mimetics, exemplify a growing arsenal of potentially effective therapeutics in controlling inflammation and the metastatic behavior of cancer.
Figures
References
-
- TOSI MF. Innate immune responses to infection. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005;116(2):241–249. - PubMed
-
- SCHON MP, LUDWIG RJ. Lymphocyte trafficking to inflamed skin - molecular mechanisms and implications for therapeutic target molecules. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets. 2005;9(2):225–243. - PubMed
-
- SPRINGER TA. Traffic signals for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration: the multistep paradigm. Cell. 1994;76(2):301–314. - PubMed
-
- KELLY M, HWANG JM, KUBES P. Modulating leukocyte recruitment in inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007 InPress. - PubMed
-
- SIMON SI, GREEN CE. Molecular mechanics and dynamics of leukocyte recruitment during inflammation. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2005;7:151–185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
