Plus disease in retinopathy of prematurity: pilot study of computer-based and expert diagnosis
- PMID: 18029210
- PMCID: PMC2190623
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaapos.2007.09.005
Plus disease in retinopathy of prematurity: pilot study of computer-based and expert diagnosis
Abstract
Purpose: To measure accuracy of plus disease diagnosis by recognized experts in retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), and to conduct a pilot study examining performance of a computer-based image analysis system, Retinal Image multiScale Analysis (RISA).
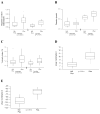
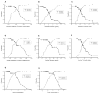
Methods: Twenty-two ROP experts independently interpreted a set of 34 wide-angle retinal images for presence of plus disease. A reference standard diagnosis based on expert consensus was defined for each image. Images were analyzed by the computer-based system using individual and linear combinations of system parameters for arterioles and venules: integrated curvature (IC), diameter, and tortuosity index (TI). Sensitivity, specificity, and receiver operating characteristic areas under the curve (AUC) for plus disease diagnosis compared with the reference standard were determined for each expert, as well as for the computer-based system.
Results: Expert sensitivity ranged from 0.308 to 1.000, specificity ranged from 0.571 to 1.000, and AUC ranged from 0.784 to 1.000. Among individual computer system parameters, venular IC had highest AUC (0.853). Among all computer system parameters, the linear combination of arteriolar IC, arteriolar TI, venular IC, venular diameter, and venular TI had highest AUC (0.967), which was greater than that of 18 (81.8%) of 22 experts.
Conclusions: Accuracy of ROP experts for plus disease diagnosis is imperfect. A computer-based image analysis system has potential to diagnose plus disease with high accuracy. Further research involving RISA system parameter cut-off values from this study are required to fully validate performance of this computer-based system compared with that of human experts.
Figures

Comment in
-
The dilemma of digital imaging in retinopathy of prematurity.J AAPOS. 2007 Dec;11(6):529-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jaapos.2007.09.014. J AAPOS. 2007. PMID: 18086430 No abstract available.
References
-
- Steinkuller PG, Du L, Gilbert C, et al. Childhood blindness. J AAPOS. 1999;3:26–32. - PubMed
-
- Committee for the classification of retinopathy of prematurity. An international classification of retinopathy of prematurity. Arch Ophthalmol. 1984;102:1130–1134. - PubMed
-
- International committee for the classification of retinopathy of prematurity. The international classification of retinopathy of prematurity revisited. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005;123:991–999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

