During infection of epithelial cells Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium undergoes a time-dependent transcriptional adaptation that results in simultaneous expression of three type 3 secretion systems
- PMID: 18031307
- PMCID: PMC2343689
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.01099.x
During infection of epithelial cells Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium undergoes a time-dependent transcriptional adaptation that results in simultaneous expression of three type 3 secretion systems
Abstract
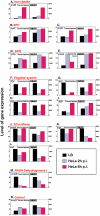
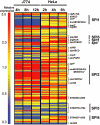
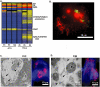
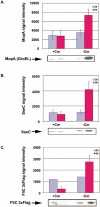
The biogenesis of the Salmonella-containing vacuole within mammalian cells has been intensively studied over recent years. However, the ability of Salmonella to sense and adapt to the intracellular environment of different types of host cells has received much less attention. To address this issue, we report the transcriptome of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium SL1344 within epithelial cells and show comparisons with Salmonella gene expression inside macrophages. We report that S. Typhimurium expresses a characteristic intracellular transcriptomic signature in response to the environments it encounters within different cell types. The signature involves the upregulation of the mgtBC, pstACS and iro genes for magnesium, phosphate and iron uptake, and Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 (SPI2). Surprisingly, in addition to SPI2, the invasion-associated SPI1 pathogenicity island and the genes involved in flagellar biosynthesis were expressed inside epithelial cells at later stages of the infection, while they were constantly downregulated in macrophage-like cells. To our knowledge, this is the first report of the simultaneous transcription of all three Type Three Secretion Systems (T3SS) within an intracellular Salmonella population. We discovered that S. Typhimurium strain SL1344 was strongly cytotoxic to epithelial cells after 6 h of infection and hypothesize that the time-dependent changes in Salmonella gene expression within epithelial cells reflects the bacterial response to host cells that have been injured by the infection process.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Coordinated regulation of expression of Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 and flagellar type III secretion systems by ATP-dependent ClpXP protease.J Bacteriol. 2008 Apr;190(7):2470-8. doi: 10.1128/JB.01385-07. Epub 2008 Feb 1. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18245288 Free PMC article.
-
Microarray-based detection of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium transposon mutants that cannot survive in macrophages and mice.Infect Immun. 2005 Sep;73(9):5438-49. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.9.5438-5449.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 16113260 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive study of the contribution of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium SPI2 effectors to bacterial colonization, survival, and replication in typhoid fever, macrophage, and epithelial cell infection models.Virulence. 2011 May-Jun;2(3):208-16. doi: 10.4161/viru.2.3.15894. Epub 2011 May 1. Virulence. 2011. PMID: 21540636 Free PMC article.
-
Polyamines are required for virulence in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e36149. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036149. Epub 2012 Apr 30. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22558361 Free PMC article.
-
Fit to dwell in many places - The growing diversity of intracellular Salmonella niches.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Aug 18;12:989451. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.989451. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36061869 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dual RNA-seq of pathogen and host.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012 Sep;10(9):618-30. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2852. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22890146 Review.
-
Host cell type-dependent translocation and PhoP-mediated positive regulation of the effector SseK1 of Salmonella enterica.Front Microbiol. 2015 Apr 29;6:396. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00396. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25972862 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA Complement of Outer Membrane Vesicles From Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Under Distinct Culture Conditions.Front Microbiol. 2018 Aug 30;9:2015. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02015. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30214435 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella Typhimurium outer membrane protein A (OmpA) renders protection from nitrosative stress of macrophages by maintaining the stability of bacterial outer membrane.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Aug 15;18(8):e1010708. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010708. eCollection 2022 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35969640 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the expression, secretion and translocation of the Salmonella enterica type III secretion system effector SteA.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26930. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026930. Epub 2011 Oct 27. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22046414 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrahams GL, Hensel M. Manipulating cellular transport and immune responses: dynamic interactions between intracellular Salmonella enterica and its host cells. Cell Microbiol. 2006;8:728–737. - PubMed
-
- Allen A. The Structure and Function of Gastrointestinal Mucous. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 1984.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

