Human papillomavirus E1 helicase interacts with the WD repeat protein p80 to promote maintenance of the viral genome in keratinocytes
- PMID: 18032488
- PMCID: PMC2224424
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01405-07
Human papillomavirus E1 helicase interacts with the WD repeat protein p80 to promote maintenance of the viral genome in keratinocytes
Abstract
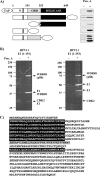
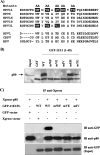
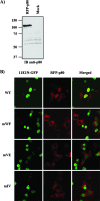
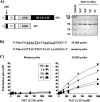
Due to the limited coding capacity of their small genomes, human papillomaviruses (HPV) rely extensively on host factors for the completion of their life cycles. Accordingly, most HPV proteins, including the replicative helicase E1, engage in multiple protein interactions. The fact that conserved regions of E1 have not yet been ascribed a function prompted us to use tandem affinity protein purification (TAP) coupled to mass spectrometry to identify novel targets of this helicase. This method led to the discovery of a novel interaction between the N-terminal 40 amino acids of HPV type 11 (HPV11) E1 and the cellular WD repeat protein p80 (WDR48). We found that interaction with p80 is conserved among E1 proteins from anogenital HPV but not among cutaneous or animal types. Colocalization studies showed that E1 can redistribute p80 from the cytoplasm to the nucleus in a manner that is dependent on the E1 nuclear localization signal. Three amino acid substitutions in E1 proteins from HPV11 and -31 were identified that abrogate binding to p80 and its relocalization to the nucleus. In HPV31 E1, these substitutions reduced but did not completely abolish transient viral DNA replication. HPV31 genomes encoding two of the mutant E1 proteins were not maintained as episomes in immortalized primary keratinocytes, whereas one encoding the third mutant protein was maintained at a very low copy number. These findings suggest that the interaction of E1 with p80 is required for efficient maintenance of the viral episome in undifferentiated keratinocytes.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Inhibition of human papillomavirus DNA replication by an E1-derived p80/UAF1-binding peptide.J Virol. 2012 Apr;86(7):3486-500. doi: 10.1128/JVI.07003-11. Epub 2012 Jan 25. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22278251 Free PMC article.
-
E1-mediated recruitment of a UAF1-USP deubiquitinase complex facilitates human papillomavirus DNA replication.J Virol. 2014 Aug;88(15):8545-55. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00379-14. Epub 2014 May 21. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24850727 Free PMC article.
-
The Cellular DNA Helicase ChlR1 Regulates Chromatin and Nuclear Matrix Attachment of the Human Papillomavirus 16 E2 Protein and High-Copy-Number Viral Genome Establishment.J Virol. 2016 Dec 16;91(1):e01853-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01853-16. Print 2017 Jan 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27795438 Free PMC article.
-
Papillomavirus E1 proteins: form, function, and features.Virus Genes. 2002 Jun;24(3):275-90. doi: 10.1023/a:1015336817836. Virus Genes. 2002. PMID: 12086149 Review.
-
The E1 proteins.Virology. 2013 Oct;445(1-2):35-56. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.07.020. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Virology. 2013. PMID: 24029589 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Virology and molecular pathogenesis of HPV (human papillomavirus)-associated oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Biochem J. 2012 Apr 15;443(2):339-53. doi: 10.1042/BJ20112017. Biochem J. 2012. PMID: 22452816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two nuclear localization signals in USP1 mediate nuclear import of the USP1/UAF1 complex.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38570. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038570. Epub 2012 Jun 6. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22701671 Free PMC article.
-
Inferring Virus-Host relationship between HPV and its host Homo sapiens using protein interaction network.Sci Rep. 2020 May 26;10(1):8719. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65837-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32457456 Free PMC article.
-
Use of a tandem affinity purification assay to detect interactions between West Nile and dengue viral proteins and proteins of the mosquito vector.Virology. 2011 Aug 15;417(1):179-87. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2011.06.002. Epub 2011 Jun 23. Virology. 2011. PMID: 21700306 Free PMC article.
-
Dengue virus capsid protein binds core histones and inhibits nucleosome formation in human liver cells.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24365. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024365. Epub 2011 Sep 1. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21909430 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amin, A. A., S. Titolo, A. Pelletier, D. Fink, M. G. Cordingley, and J. Archambault. 2000. Identification of domains of the HPV11 E1 protein required for DNA replication in vitro. Virology 272137-150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

