Species-specific restriction of apobec3-mediated hypermutation
- PMID: 18032489
- PMCID: PMC2224457
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01371-07
Species-specific restriction of apobec3-mediated hypermutation
Abstract
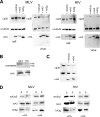
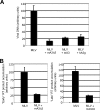
Apobec proteins are a family of cellular cytidine deaminases, among which several members have been shown to have potent antiviral properties. This antiviral activity is associated with the ability to cause hypermutation of retroviral cDNA. However, recent research has indicated that Apobec proteins are also able to inhibit retroviruses by other mechanisms that are independent of their deaminase activity. We have compared the antiviral activities of human and murine Apobec3 (A3) proteins, and we have found that, consistent with previous reports, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is able to resist human A3G but is sensitive to murine A3, whereas murine leukemia virus (MLV) is relatively resistant to murine A3 (mA3) but sensitive to human A3G. In contrast to previous studies, we observed that mA3 is packaged efficiently into MLV particles. The C-terminal cytidine deaminase domain (CDD2) is required for packaging of mA3 into MLV particles, and packaging did not depend on the MLV viral RNA. However, mA3 packed into MLV particles failed to cause hypermutation of viral DNA, indicating that its deaminase activity is blocked or inhibited. hA3G also caused significantly less hypermutation of MLV than of HIV DNA. Both mA3 and the splice variant mA3Delta5 exhibited some residual antiviral activity against MLV and caused a reduction in the ability of MLV particles to generate reverse transcription products. These results suggest that MLV has evolved specific mechanisms to block the ability of Apobec proteins to mediate deaminase-dependent hypermutation.
Figures
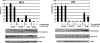


Similar articles
-
Interactions of murine APOBEC3 and human APOBEC3G with murine leukemia viruses.J Virol. 2008 Jul;82(13):6566-75. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01357-07. Epub 2008 Apr 30. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18448535 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and biological studies of mouse APOBEC3.J Virol. 2014 Apr;88(7):3850-60. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03456-13. Epub 2014 Jan 22. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24453360 Free PMC article.
-
The incorporation of APOBEC3 proteins into murine leukemia viruses.Virology. 2008 Aug 15;378(1):69-78. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.05.006. Epub 2008 Jun 24. Virology. 2008. PMID: 18572219
-
Cytidine deaminases as a weapon against retroviruses and a new target for antiviral therapy.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2008 Mar;8(3):231-8. doi: 10.2174/138955708783744047. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18336343 Review.
-
APOBEC3 proteins and reverse transcription.Virus Res. 2008 Jun;134(1-2):74-85. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2007.12.022. Epub 2008 Feb 11. Virus Res. 2008. PMID: 18262674 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of a highly sensitive strand-specific quantitative PCR to identify abortive replication in the mouse model of respiratory syncytial virus disease.Virol J. 2010 Sep 22;7:250. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-250. Virol J. 2010. PMID: 20860795 Free PMC article.
-
APOBEC3G and APOBEC3F require an endogenous cofactor to block HIV-1 replication.PLoS Pathog. 2008 Jul 4;4(7):e1000095. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000095. PLoS Pathog. 2008. PMID: 18604271 Free PMC article.
-
Tumultuous relationship between the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 viral infectivity factor (Vif) and the human APOBEC-3G and APOBEC-3F restriction factors.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009 Jun;73(2):211-32. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00040-08. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19487726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myelodysplasia after clonal hematopoiesis with APOBEC3-mediated CYBB inactivation in retroviral gene therapy for X-CGD.Mol Ther. 2023 Dec 6;31(12):3424-3440. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.09.004. Epub 2023 Sep 13. Mol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37705244 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse APOBEC3 expression in NIH 3T3 cells mediates hypermutation of AKV murine leukemia virus.Virology. 2018 May;518:377-384. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2018.03.014. Epub 2018 Mar 30. Virology. 2018. PMID: 29605684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abudu, A., A. Takaori-Kondo, T. Izumi, K. Shirakawa, M. Kobayashi, A. Sasada, K. Fukunaga, and T. Uchiyama. 2006. Murine retrovirus escapes from murine APOBEC3 via two distinct novel mechanisms. Curr. Biol. 161565-1570. - PubMed
-
- Bishop, K. N., R. K. Holmes, A. M. Sheehy, N. O. Davidson, S. J. Cho, and M. H. Malim. 2004. Cytidine deamination of retroviral DNA by diverse APOBEC proteins. Curr. Biol. 141392-1396. - PubMed
-
- Chen, H., C. E. Lilley, Q. Yu, D. V. Lee, J. Chou, I. Narvaiza, N. R. Landau, and M. D. Weitzman. 2006. APOBEC3A is a potent inhibitor of adeno-associated virus and retrotransposons. Curr. Biol. 16480-485. - PubMed
-
- Chiu, Y. L., and W. C. Greene. 2006. Multifaceted antiviral actions of APOBEC3 cytidine deaminases. Trends Immunol. 27291-297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

