Antiinflammatory glucocorticoid receptor ligand with reduced side effects exhibits an altered protein-protein interaction profile
- PMID: 18032610
- PMCID: PMC2148275
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0705517104
Antiinflammatory glucocorticoid receptor ligand with reduced side effects exhibits an altered protein-protein interaction profile
Abstract
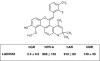
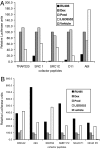
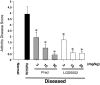
Glucocorticoids are commonly used antiinflammatory agents whose use is limited by side effects. We have developed a series of glucocorticoid receptor (GR) ligands that retain the strong antiinflammatory activity of conventional glucocorticoids with reduced side effects. We present a compound, LGD5552, that binds the receptor efficiently and strongly represses inflammatory gene expression. LGD5552 bound to GR activates gene expression somewhat differently than glucocorticoids. It activates some genes with an efficacy similar to that of the glucocorticoids. However, other glucocorticoid-activated genes are not regulated by LGD5552. These differences may be because of the more efficient binding of corepressor in the presence of LGD5552, compared with glucocorticoid agonists. This class of nonsteroidal, GR-dependent antiinflammatory drugs may offer a safer alternative to steroidal glucocorticoids in the treatment of inflammatory disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors are or were employed by Ligand Pharmaceuticals.
Figures

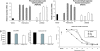

Similar articles
-
LGD-5552, an antiinflammatory glucocorticoid receptor ligand with reduced side effects, in vivo.Endocrinology. 2008 May;149(5):2080-9. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-1353. Epub 2008 Jan 24. Endocrinology. 2008. PMID: 18218700
-
The search for safer glucocorticoid receptor ligands.Endocr Rev. 2005 May;26(3):452-64. doi: 10.1210/er.2005-0002. Epub 2005 Apr 6. Endocr Rev. 2005. PMID: 15814846 Review.
-
A novel antiinflammatory maintains glucocorticoid efficacy with reduced side effects.Mol Endocrinol. 2003 May;17(5):860-9. doi: 10.1210/me.2002-0355. Epub 2003 Feb 13. Mol Endocrinol. 2003. PMID: 12586843
-
Glucocorticoid receptor in stromal cells is essential for glucocorticoid-mediated suppression of inflammation in arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2018 Nov;77(11):1610-1618. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212762. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018. PMID: 29997111 Free PMC article.
-
Classic glucocorticoids versus non-steroidal glucocorticoid receptor modulators: survival of the fittest regulator of the immune system?Brain Behav Immun. 2010 Oct;24(7):1035-42. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2010.06.010. Epub 2010 Jun 25. Brain Behav Immun. 2010. PMID: 20600811 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of selective glucocorticoid receptor modulators are partially dependent on up-regulation of dual specificity phosphatase 1.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Feb;165(4b):1124-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01574.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21718312 Free PMC article.
-
Org 214007-0: a novel non-steroidal selective glucocorticoid receptor modulator with full anti-inflammatory properties and improved therapeutic index.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e48385. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048385. Epub 2012 Nov 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23152771 Free PMC article.
-
The multiple facets of glucocorticoid action in rheumatoid arthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012 Nov;8(11):645-55. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2012.166. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012. PMID: 23045254 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of selective glucocorticoid receptor modulators in comparison to glucocorticoids in arthritis, a systematic review.PLoS One. 2017 Dec 21;12(12):e0188810. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188810. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29267302 Free PMC article.
-
Selective amplification of glucocorticoid anti-inflammatory activity through synergistic multi-target action of a combination drug.Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(1):R12. doi: 10.1186/ar2602. Epub 2009 Jan 26. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19171052 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rosen J, Miner JN. Endocr Rev. 2005;26:452–464. - PubMed
-
- Collingwood TN, Urnov FD, Wolffe AP. J Mol Endocrinol. 1999;23:255–275. - PubMed
-
- Herrlich P. Oncogene. 2001;20:2465–2475. - PubMed
-
- Iwasaki K, Mishima E, Miura M, Sakai N, Shimao S. J Dermatol Sci. 1995;10:151–158. - PubMed
-
- Miner JN, Hong MH, Negro-Vilar A. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2005;14:1527–1545. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Medical

