The structural basis of cyclic diguanylate signal transduction by PilZ domains
- PMID: 18034161
- PMCID: PMC2140105
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601918
The structural basis of cyclic diguanylate signal transduction by PilZ domains
Abstract
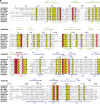
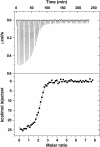
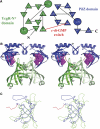
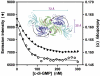
The second messenger cyclic diguanylate (c-di-GMP) controls the transition between motile and sessile growth in eubacteria, but little is known about the proteins that sense its concentration. Bioinformatics analyses suggested that PilZ domains bind c-di-GMP and allosterically modulate effector pathways. We have determined a 1.9 A crystal structure of c-di-GMP bound to VCA0042/PlzD, a PilZ domain-containing protein from Vibrio cholerae. Either this protein or another specific PilZ domain-containing protein is required for V. cholerae to efficiently infect mice. VCA0042/PlzD comprises a C-terminal PilZ domain plus an N-terminal domain with a similar beta-barrel fold. C-di-GMP contacts seven of the nine strongly conserved residues in the PilZ domain, including three in a seven-residue long N-terminal loop that undergoes a conformational switch as it wraps around c-di-GMP. This switch brings the PilZ domain into close apposition with the N-terminal domain, forming a new allosteric interaction surface that spans these domains and the c-di-GMP at their interface. The very small size of the N-terminal conformational switch is likely to explain the facile evolutionary diversification of the PilZ domain.
Figures


References
-
- Ades SE (1995) The engrailed homeodomain: determinants of DNA-binding affinity and specificity. PhD Thesis. Department of Biology, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA
-
- Amikam D, Galperin MY (2006) PilZ domain is part of the bacterial c-di-GMP binding protein. Bioinformatics 22: 3–6 - PubMed
-
- Ausmees N, Mayer R, Weinhouse H, Volman G, Amikam D, Benziman M, Lindberg M (2001) Genetic data indicate that proteins containing the GGDEF domain possess diguanylate cyclase activity. FEMS Microbiol Lett 204: 163–167 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

