Anti-chromatin antibodies drive in vivo antigen-specific activation and somatic hypermutation of rheumatoid factor B cells at extrafollicular sites
- PMID: 18034429
- PMCID: PMC3516908
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.200737752
Anti-chromatin antibodies drive in vivo antigen-specific activation and somatic hypermutation of rheumatoid factor B cells at extrafollicular sites
Abstract
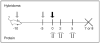
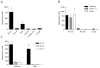
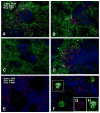
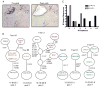
A dominant type of spontaneous autoreactive B cell activation in murine lupus is the extrafollicular generation of plasmablasts. The factors governing such activation have been difficult to identify due to the stochastic onset and chronic nature of the response. Thus, the ability to induce a similar autoreactive B cell response with a known autoantigen in vivo would be a powerful tool in deciphering how autoimmune responses are initiated. We report here the establishment and characterization of a system to initiate autoreactive extrafollicular B cell responses, using IgG anti-chromatin antibodies, that closely mirrors the spontaneous response. We demonstrate that exogenously administered anti-chromatin antibody, presumably by forming immune complexes with released nuclear material, drives activation of rheumatoid factor B cells in AM14 Tg mice. Anti-chromatin elicits autoreactive B cell activation and development into antibody-forming cells at the T zone/red pulp border. Plasmablast generation occurs equally in BALB/c, MRL/+ and MRL/lpr mice, indicating that an autoimmune-prone genetic background is not required for the induced response. Importantly, infused IgG anti-chromatin induces somatic hypermutation in the absence of a GC response, thus proving the extrafollicular somatic hypermutation pathway. This system provides a window on the initiation of an autoantibody response and reveals authentic initiators of it.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Autoreactive B cells get activated in extrafollicular sites.Eur J Immunol. 2007 Dec;37(12):3330-3. doi: 10.1002/eji.200737971. Eur J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 18050163
References
-
- Tan EM. Antinuclear antibodies: diagnostic markers for autoimmune diseases and probes for cell biology. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:93–151. - PubMed
-
- Shlomchik MJ, Craft J, Mamula MJ. From T to B and back again: positive feedback in systemic autoimmune disease. Nature Reviews Immunology. 2001;1:147–153. - PubMed
-
- Chan O, Shlomchik MJ. A new role for B cells in systemic autoimmunity: B cells promote spontaneous T cell activation in MRL-lpr/lpr mice. J Immunol. 1998;160:51–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

