A quantitative proteomic analysis of mitochondrial participation in p19 cell neuronal differentiation
- PMID: 18034457
- PMCID: PMC2547413
- DOI: 10.1021/pr070300g
A quantitative proteomic analysis of mitochondrial participation in p19 cell neuronal differentiation
Abstract
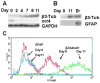
A quantitative proteomic analysis of changes in protein expression accompanying the differentiation of P19 mouse embryonal carcinoma cells into neuron-like cells using isobaric tag technology coupled with LC-MS/MS revealed protein changes reflecting withdrawal from the cell cycle accompanied by a dynamic reorganization of the cytoskeleton and an up-regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis. Further study of quantitative changes in abundance of individual proteins in a purified mitochondrial fraction showed that most mitochondrial proteins increased significantly in abundance. A set of chaperone proteins did not participate in this increase, suggesting that neuron-like cells are relatively deficient in mitochondrial chaperones. We developed a procedure to account for differences in recovery of mitochondrial proteins during purification of organelles from distinct cell or tissue sources. Proteomic data supported by RT-PCR analysis suggests that enhanced mitochondrial biogenesis during neuronal differentiation may reflect a large increase in expression of PGC-1alpha combined with down-regulation of its negative regulator, p160 Mybbp1a.
Figures






References
-
- Bain G, Ray WJ, Yao M, Gottlieb DI. From Embryonal Carcinoma Cells to Neurons: The P19 Pathway. BioEssays. 1994;16:343–348. - PubMed
-
- McBurney MW, Rogers BJ. Isolation of male embryonic carcinoma cells and their chromosome replication patterns. Dev Biol. 1982;89:503–508. - PubMed
-
- Rossant J, McBurney MW. The developmental potential of a euploid male teratocarcinoma cell line after blastocyst injection. J Embryol Exp Morph. 1982;70:99–112. - PubMed
-
- Meeks JP, Mennerick S. Feeding hungry neurons: astrocytes deliver food for thought. Neuron. 2003;37(2):187–9. - PubMed
-
- Voutsinos-Porche B, Bonvento G, Tanaka K, Steiner P, Welker E, Chatton JY, Magistretti PJ, Pellerin L. Glial glutamate transporters mediate a functional metabolic crosstalk between neurons and astrocytes in the mouse developing cortex. Neuron. 2003;37(2):275–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

