An n-3 fatty acid deficient diet affects mouse spatial learning in the Barnes circular maze
- PMID: 18037280
- PMCID: PMC2194649
- DOI: 10.1016/j.plefa.2007.10.013
An n-3 fatty acid deficient diet affects mouse spatial learning in the Barnes circular maze
Abstract
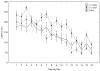
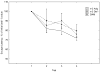
Deficiency in n-3 fatty acids has been accomplished through the use of an artificial rearing method in which ICR mouse pups were hand fed a deficient diet starting from the 2nd day of life. There was a 51% loss of total brain DHA in mice with an n-3 fatty acid-deficient diet relative to those with a diet sufficient in n-3 fatty acids. n-3 fatty acid adequate and deficient mice did not differ in terms of locomotor activity in the open field test or in anxiety-related behavior in the elevated plus maze. The n-3 fatty acid-deficient mice demonstrated impaired learning in the reference-memory version of the Barnes circular maze as they spent more time and made more errors in search of an escape tunnel. No difference in performance between all dietary groups in the cued and working memory version of the Barnes maze was observed. This indicated that motivational, motor and sensory factors did not contribute to the reference memory impairment.
Figures


References
-
- Salem N., Jr . Omega-3 fatty acids: molecular and biochemical aspects. In: Spiller GA, Scala J, editors. Current Topics in Nutrition and Disease: New Protective Roles for Selected Nutrients. Alan R Liss; New York: 1989. pp. 109–228.
-
- Mohrhauer H, Holman RT. Alteration of the fatty acid composition of brain lipids by varying levels of dietary essential fatty acids. J Neurochem. 1963;10:523–530. - PubMed
-
- Galli C, Trzeciak HI, Paoletti R. Effects of dietary fatty acids on the fatty acid composition of brain ethanolamine phosphoglyceride: Reciprocal replacement of n-6 and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971;248:449–454.
-
- Yamamoto N, Saitoh M, Moriguchi A, Nomura M, Okuyama H. Effect of dietary alpha-linolenate/linoleate balance on brain lipid compositions and learning ability of rats. J Lipid Res. 1987;28:144–151. - PubMed
-
- Bourre JM, Francois M, Youyou A, Dumont O, Piciotti M, Pascal G, Durand G. The effects of dietary alpha-linolenic acid on the composition of nerve membranes, enzymatic activity, amplitude of electrophysiological parameters, resistance to poisons and performance of learning tasks in rats. J Nutr. 1989;119:1880–1892. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

