Data-driven clustering reveals a fundamental subdivision of the human cortex into two global systems
- PMID: 18037453
- PMCID: PMC4468071
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.10.003
Data-driven clustering reveals a fundamental subdivision of the human cortex into two global systems
Abstract
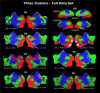
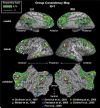
Global organizational principles are critical for understanding cortical functionality. Recently, we proposed a global sub-division of the posterior cortex into two large-scale systems. One system, labeled extrinsic, comprises the sensory-motor cortex, and is associated with the external environment. The second system, labeled intrinsic, overlaps substantially with the previously described "default-mode" network, and is likely associated with inner-oriented processing. This global partition of the cerebral cortex emerged from hemodynamic imaging data the analysis of which was constrained by pre-determined hypotheses. Here we applied a hypothesis-free, unsupervised two-class clustering algorithm (k-means) to a large set of fMRI data. The two clusters delineated by this unsupervised hypothesis-free procedure showed high anatomical consistency across individuals, and their cortical topography coincided largely with the previously determined extrinsic and intrinsic systems. These new clustering-based results confirm that the intrinsic-extrinsic subdivision constitutes a fundamental cortical divide.
Figures



References
-
- Amedi A, Malach R, Pascual-Leone A. Negative BOLD differentiates visual imagery and perception. Neuron. 2005;48(5):859–872. - PubMed
-
- Arieli A, Sterkin A, Grinvald A, Aertsen A. Dynamics of ongoing activity: explanation of the large variability in evoked cortical responses. Science. 1996;273(5283):1868–1871. - PubMed
-
- Arndt S, Cizadlo T, O'Leary D, Gold S, Andreasen NC. Normalizing counts and cerebral blood flow intensity in functional imaging studies of the human brain. Neuroimage. 1996;3(3 Pt 1):175–184. - PubMed
-
- Bartels A, Zeki S. Brain dynamics during natural viewing conditions-A new guide for mapping connectivity in vivo. Neuroimage. 2005;24(2):339–349. - PubMed
-
- Baumgartner R, Scarth G, Teichtmeister C, Somorjai R, Moser E. Fuzzy clustering of gradient-echo functional MRI in the human visual cortex. Part I: reproducibility. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1997;7(6):1094–1101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

