Cell penetrating peptide conjugates of steric block oligonucleotides
- PMID: 18037527
- PMCID: PMC7103303
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2007.09.002
Cell penetrating peptide conjugates of steric block oligonucleotides
Abstract
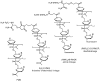
Charge neutral steric block oligonucleotide analogues, such as peptide nucleic acids (PNA) or phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers (PMO), have promising biological and pharmacological properties for antisense applications, such as for example in mRNA splicing redirection. However, cellular uptake of free oligomers is poor and the utility of conjugates of PNA or PMO to cell penetrating peptides (CPP), such as Tat or Penetratin, is limited by endosomal sequestration. Two new families of arginine-rich CPPs named (R-Ahx-R)(4) AhxB and R(6)Pen allow efficient nuclear delivery of splice correcting PNA and PMO at micromolar concentrations in the absence of endosomolytic agents. The in vivo efficacy of (R-Ahx-R)(4) AhxB PMO conjugates has been demonstrated in mouse models of Duchenne muscular dystrophy and in various viral infections.
Figures


References
-
- Kurreck J. Antisense technologies. Improvement through novel chemical modifications. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003;270:1628–1644. - PubMed
-
- Gleave M.E., Monia B.P. Antisense therapy for cancer. Nat. Rev., Cancer. 2005;5:468–479. - PubMed
-
- Baker B.F., Lot S.S., Condon T.P., Cheng-Flourney S., Lesnik E.A., Sasmor H.M., Bennett C.F. 2'-O-(2-methoxy)ethyl-modified anti-intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) oligonucleotides selectively increase the ICAM-1 mRNA level and inhibit formation of the ICAM-1 translation initiation complex in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:11994–12000. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

