Regulation of Rap1 activity by RapGAP1 controls cell adhesion at the front of chemotaxing cells
- PMID: 18039932
- PMCID: PMC2099181
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200705068
Regulation of Rap1 activity by RapGAP1 controls cell adhesion at the front of chemotaxing cells
Abstract
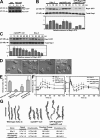
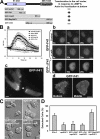
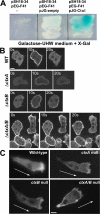
Spatial and temporal regulation of Rap1 is required for proper myosin assembly and cell adhesion during cell migration in Dictyostelium discoideum. Here, we identify a Rap1 guanosine triphosphatase-activating protein (GAP; RapGAP1) that helps mediate cell adhesion by negatively regulating Rap1 at the leading edge. Defects in spatial regulation of the cell attachment at the leading edge in rapGAP1- (null) cells or cells overexpressing RapGAP1 (RapGAP1(OE)) lead to defective chemotaxis. rapGAP1- cells have extended chemoattractant-mediated Rap1 activation kinetics and decreased MyoII assembly, whereas RapGAP1(OE) cells show reciprocal phenotypes. We see that RapGAP1 translocates to the cell cortex in response to chemoattractant stimulation and localizes to the leading edge of chemotaxing cells via an F-actin-dependent pathway. RapGAP1 localization is negatively regulated by Ctx, an F-actin bundling protein that functions during cytokinesis. Loss of Ctx leads to constitutive and uniform RapGAP1 cortical localization. We suggest that RapGAP1 functions in the spatial and temporal regulation of attachment sites through MyoII assembly via regulation of Rap1-guanosine triphosphate.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cell migration: regulation of cytoskeleton by Rap1 in Dictyostelium discoideum.J Microbiol. 2012 Aug;50(4):555-61. doi: 10.1007/s12275-012-2246-7. Epub 2012 Aug 25. J Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22923101 Review.
-
Rap1 controls cell adhesion and cell motility through the regulation of myosin II.J Cell Biol. 2007 Mar 26;176(7):1021-33. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200607072. Epub 2007 Mar 19. J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17371831 Free PMC article.
-
A negative feedback loop between small GTPase Rap1 and mammalian tumor suppressor homologue KrsB regulates cell-substrate adhesion in Dictyostelium.Mol Biol Cell. 2025 Apr 1;36(4):ar43. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E24-11-0507. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Mol Biol Cell. 2025. PMID: 39937679 Free PMC article.
-
Rap1-dependent pathways coordinate cytokinesis in Dictyostelium.Mol Biol Cell. 2014 Dec 15;25(25):4195-204. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-08-1285. Epub 2014 Oct 8. Mol Biol Cell. 2014. PMID: 25298405 Free PMC article.
-
Activation and function of the Rap1 GTPase in B lymphocytes.Int Rev Immunol. 2001;20(6):763-89. doi: 10.3109/08830180109045589. Int Rev Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11913949 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphatidic acid-dependent localization and basal de-phosphorylation of RA-GEFs regulate lymphocyte trafficking.BMC Biol. 2020 Jun 29;18(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12915-020-00809-0. BMC Biol. 2020. PMID: 32600317 Free PMC article.
-
G protein betagamma subunits regulate cell adhesion through Rap1a and its effector Radil.J Biol Chem. 2010 Feb 26;285(9):6538-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.069948. Epub 2010 Jan 4. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20048162 Free PMC article.
-
Cell migration: regulation of cytoskeleton by Rap1 in Dictyostelium discoideum.J Microbiol. 2012 Aug;50(4):555-61. doi: 10.1007/s12275-012-2246-7. Epub 2012 Aug 25. J Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22923101 Review.
-
Proteomic identification of phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5) triphosphate-binding proteins in Dictyostelium discoideum.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jun 29;107(26):11829-34. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1006153107. Epub 2010 Jun 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20547830 Free PMC article.
-
Short- and long-term memory of moving amoeboid cells.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 11;16(2):e0246345. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246345. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33571271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bos, J.L. 2005. Linking Rap to cell adhesion. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 17:123–128. - PubMed
-
- Brinkmann, T., O. Daumke, U. Herbrand, D. Kuhlmann, P. Stege, M.R. Ahmadian, and A. Wittinghofer. 2002. Rap-specific GTPase activating protein follows an alternative mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 277:12525–12531. - PubMed
-
- Chisholm, R.L., and R.A. Firtel. 2004. Insights into morphogenesis from a simple developmental system. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 5:531–541. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

