HDAC inhibitor PCI-24781 decreases RAD51 expression and inhibits homologous recombination
- PMID: 18042714
- PMCID: PMC2148315
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0707828104
HDAC inhibitor PCI-24781 decreases RAD51 expression and inhibits homologous recombination
Abstract
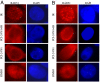
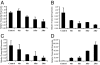
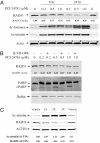
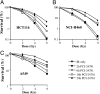
Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors such as the phenyl hydroxamic acid PCI-24781 have emerged recently as a class of therapeutic agents for the treatment of cancer. Recent data showing synergy of HDAC inhibitors with ionizing radiation and other DNA-damaging agents have suggested that HDAC inhibitors may act, in part, by inhibiting DNA repair. Here we present evidence that HDAC enzymes are important for homologous recombinational repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Combination studies of PCI-24781 with the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor PJ34, an agent thought to produce lesions repaired by homologous recombination (HR), resulted in a synergistic effect on apoptosis. Immunofluorescence analysis demonstrated that HDAC inhibition caused a complete inhibition of subnuclear repair foci in response to ionizing radiation. Mechanistic investigations revealed that inhibition of HDAC enzymes by PCI-24781 led to a significant reduction in the transcription of genes specifically associated with HR, including RAD51. RAD51 protein levels were significantly decreased after 24 h of drug exposure both in vitro and in vivo. Consistent with inhibition of HR, treatment with PCI-24781 resulted in a decreased ability to perform homology directed repair of I-SceI-induced chromosome breaks in transfected CHO cells. In addition, an enhancement of cell killing was observed in Ku mutant cells lacking functional nonhomologous end joining compared with WT cells. Together these results demonstrate that HDAC enzymes are critically important to enable functional HR by controlling the expression of HR-related genes and promoting the proper assembly of HR-directed subnuclear foci.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Buggy JJ, Cao ZA, Bass KE, Verner E, Balasubramanian S, Liu L, Schultz BE, Young PR, Dalrymple SA. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006;5:1309–1317. - PubMed
-
- Bolden JE, Peart MJ, Johnstone RW. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:769–784. - PubMed
-
- Drummond DC, Noble CO, Kirpotin DB, Guo Z, Scott GK, Benz CC. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2004;45:495–528. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

