Role of matrix metalloproteinase-2 in newborn mouse lungs under hypoxic conditions
- PMID: 18043506
- PMCID: PMC2517580
- DOI: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e31815b690d
Role of matrix metalloproteinase-2 in newborn mouse lungs under hypoxic conditions
Abstract
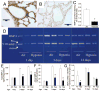
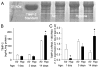
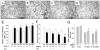
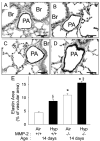
Hypoxia impairs normal neonatal pulmonary artery remodeling and alveolar development. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2), which regulates collagen breakdown, is important during development. Our objective was to test the hypothesis that hypoxia attenuates the normal postnatal increase in MMP-2 and evaluate alveolar development and pulmonary arterial remodeling in Mmp2 mice. C57BL/6 wild-type (WT), Mmp2, Mmp2, and MMP-inhibited (with doxycycline) mice were exposed to hypoxia (12% O2) or air from birth to 2 wk of age. Pulmonary arterial remodeling, alveolar development, and vascular collagen and elastin were evaluated. MMP-2 was estimated by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, immunohistochemistry, and zymography. We observed that 1) in WT mice, hypoxia led to thicker-walled pulmonary arteries and impaired alveolarization, accompanied by decreased MMP-2 and increased tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 (TIMP-2); 2) Mmp2 mice in air had thicker-walled arteries, impaired alveolarization, and increased perivascular collagen and elastin compared with WT; 3) hypoxia further inhibited alveolarization but did not alter arterial thickening in Mmp2 mice. Mmp2 and MMP-inhibited mice also had thicker-walled arteries than WT in air, but alveolarization was not different. We conclude that hypoxia reduces the postnatal MMP-2 increase in the lung, which may contribute to abnormal pulmonary arterial remodeling and impaired alveolarization.
Figures
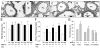

References
-
- Haworth SG, Hislop AA. Lung development-the effects of chronic hypoxia. Semin Neonatol. 2003;8:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Walsh-Sukys MC. Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. The black box revisited. Clin Perinatol. 1993;20:127–143. - PubMed
-
- Goodman G, Perkin RM, Anas NG, Sperling DR, Hicks DA, Rowen M. Pulmonary hypertension in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr. 1988;112:67–71. - PubMed
-
- Hoffmeister HM, Apitz J, Hoffmeister HE, Fischbach H. The correlation between blood pressure and morphometric findings in children with congenital heart disease and pulmonary hypertension. Basic Res Cardiol. 1981;76:647–656. - PubMed
-
- Steinhorn RH, Fineman JR. The pathophysiology of pulmonary hypertension in congenital heart disease. Artif Organs. 1999;23:970–974. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL-50147/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-44195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HD046513/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL056046/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007457/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL045990/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-45990/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R29 HL056046/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-07457/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL044195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR 15490/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HL-56046/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR015490/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

