Proteomic shifts in embryonic stem cells with gene dose modifications suggest the presence of balancer proteins in protein regulatory networks
- PMID: 18043732
- PMCID: PMC2077926
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001218
Proteomic shifts in embryonic stem cells with gene dose modifications suggest the presence of balancer proteins in protein regulatory networks
Abstract
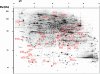
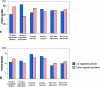
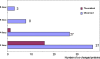
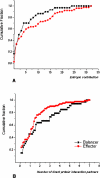
Large numbers of protein expression changes are usually observed in mouse models for neurodegenerative diseases, even when only a single gene was mutated in each case. To study the effect of gene dose alterations on the cellular proteome, we carried out a proteomic investigation on murine embryonic stem cells that either overexpressed individual genes or displayed aneuploidy over a genomic region encompassing 14 genes. The number of variant proteins detected per cell line ranged between 70 and 110, and did not correlate with the number of modified genes. In cell lines with single gene mutations, up and down-regulated proteins were always in balance in comparison to parental cell lines regarding number as well as concentration of differentially expressed proteins. In contrast, dose alteration of 14 genes resulted in an unequal number of up and down-regulated proteins, though the balance was kept at the level of protein concentration. We propose that the observed protein changes might partially be explained by a proteomic network response. Hence, we hypothesize the existence of a class of "balancer" proteins within the proteomic network, defined as proteins that buffer or cushion a system, and thus oppose multiple system disturbances. Through database queries and resilience analysis of the protein interaction network, we found that potential balancer proteins are of high cellular abundance, possess a low number of direct interaction partners, and show great allelic variation. Moreover, balancer proteins contribute more heavily to the network entropy, and thus are of high importance in terms of system resilience. We propose that the "elasticity" of the proteomic regulatory network mediated by balancer proteins may compensate for changes that occur under diseased conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Goldberg MS, Fleming SM, Palacino JJ, Cepeda C, Lam HA, et al. Parkin-deficient mice exhibit nigrostriatal deficits but not loss of dopaminergic neurons. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:43628–43635. Epub 42003 Aug 43620. - PubMed
-
- Mangiarini L, Sathasivam K, Seller M, Cozens B, Harper A, et al. Exon 1 of the HD gene with an expanded CAG repeat is sufficient to cause a progressive neurological phenotype in transgenic mice. Cell. 1996;87:493–506. - PubMed
-
- Palacino JJ, Sagi D, Goldberg MS, Krauss S, Motz C, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative damage in parkin-deficient mice. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:18614–18622. - PubMed
-
- Zabel C, Klose J. Influence of Huntington's Disease on the Human and Mouse Proteome. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2004;61:241–283. - PubMed
-
- Periquet M, Corti O, Jacquier S, Brice A. Proteomic analysis of parkin knockout mice: alterations in energy metabolism, protein handling and synaptic function. J Neurochem. 2005;95:1259–1276. Epub 2005 Sep 1257. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

