Telomerase confers resistance to caspase-mediated apoptosis
- PMID: 18044112
- PMCID: PMC2695162
- DOI: 10.2147/ciia.2006.1.2.155
Telomerase confers resistance to caspase-mediated apoptosis
Abstract
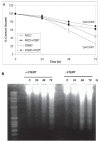
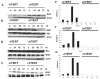
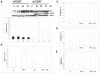
There is growing evidence that accelerated telomeric attrition and/or aberrant telomerase activity contributes to pathogenesis in a number of diseases. Likewise, there is increasing interest to develop new therapies to restore or replace dysfunctional cells characterized by short telomeric length using telomerase-positive counterparts or stem cells. While telomerase adds telomeric repeats de novo contributing to enhanced proliferative capacity and lifespan, it may also increase cellular survival by conferring resistance to apoptosis. Consequently, we sought to determine the involvement of telomerase for reduced apoptosis using ovarian surface epithelial cells. We found that expression of hTERT, the catalytic component of telomerase, was sufficient and specific to reduce caspase-mediated cellular apoptosis. Further, hTERT expression reduced activation of caspases 3, 8, and 9, reduced expression of pro-apoptotic mitochondrial proteins t-BID, BAD, and BAX and increased expression of the anti-apoptotic mitochondrial protein, Bcl-2. The ability of telomerase to suppress caspase-mediated apoptosis was p-jnk dependent since abrogation of jnk expression with jip abolished resistance to apoptosis. Consequently, these findings indicate that telomerase may promote cellular survival in epithelial cells by suppressing jnk-dependent caspase-mediated apoptosis.
Figures



References
-
- Alfonso-De Matte MY, Cheng JQ, Kruk PA. Ultraviolet irradiation-and dimethyl sulfoxide-induced telomerase activity in ovarian epithelial cell lines. Exp Cell Res. 2001;267:13–27. - PubMed
-
- Alfonso-De Matte MY, Moses-Soto H, Kruk PA. Calcium induces telomerase activity in ovarian epithelial cell lines. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2002;399:239–44. - PubMed
-
- Alfonso-De Matte MY, Yang H, Cheng JQ, et al. C-Jun kinase-mediated regulation of telomerase in ovarian surface epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 2002;62:4575–8. - PubMed
-
- Alfonso-De Matte MY, Kruk PA. Phosphotidylinositol-triphosphate kinase- and c-jun N-terminal kinase-dependent induction of telomerase by calcium requires pyk2. Cancer Res. 2004;64:23–6. - PubMed
-
- Allsopp RC, Chang E, Kashefi-Aazam M, et al. Telomere shortening is associated with cell division in vitro and in vivo. Exp Cell Res. 1995;220:194–200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

