Capillary-based multi nanoelectrospray emitters: improvements in ion transmission efficiency and implementation with capillary reversed-phase LC-ESI-MS
- PMID: 18044958
- PMCID: PMC2587435
- DOI: 10.1021/ac701647s
Capillary-based multi nanoelectrospray emitters: improvements in ion transmission efficiency and implementation with capillary reversed-phase LC-ESI-MS
Abstract
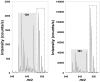
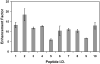
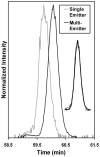
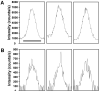
We describe the coupling of liquid chromatography (LC) separations with mass spectrometry (MS) using nanoelectrospray ionization (nano-ESI) multiemitters. The array of 19 emitters reduced the flow rate delivered to each emitter, allowing the enhanced sensitivity that is characteristic of nano-ESI to be extended to higher flow rate separations. The signal for tryptic fragments from proteins spiked into a human plasma sample increased 11-fold on average when the multiemitters were employed, due to increased ionization efficiency and improved ion transfer efficiency through a newly designed heated multicapillary MS inlet. Additionally, the LC peak signal-to-noise ratio increased approximately 7-fold when the multiemitter configuration was used. The low dead volume of the emitter arrays preserved peak shape and resolution for robust capillary LC separations using total flow rates of 2 microL/min.
Figures



References
-
- Smith RD, Shen Y, Tang K. Accounts Chem. Res. 2004;37:269–278. - PubMed
-
- Manisali I, Chen DDY, Schneider BB. Trends Anal. Chem. 2006;25:243–256.
-
- Smith RD, Loo JA, Edmonds CG, Barinaga CJ, Udseth HR. Anal. Chem. 1990;62:882–899. - PubMed
-
- Kebarle P, Tang L. Anal. Chem. 1993;65:A972–A986.
-
- Cech NB, Enke CG. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2001;20:362–387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

