The formation pathway of tetramolecular G-quadruplexes
- PMID: 18045788
- PMCID: PMC2241855
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm1050
The formation pathway of tetramolecular G-quadruplexes
Abstract
Oligonucleotides containing guanosine stretches associate into tetrameric structures stabilized by monovalent ions. In order to describe the sequence of reactions leading to association of four identical strands, we measured by NMR the formation and dissociation rates of (TGnT)4 quadruplexes (n = 3-6), their dissociation constants and the reaction orders for quadruplex formation. The quadruplex formation rates increase with the salt concentration but weakly depend on the nature (K+, Na+ or Li+) of the counter ions. The activation energies for quadruplex formation are negative. The quadruplex lifetimes strongly increase with the G-tract length and are much more longer in K+ solution than in Na+ or Li+ solutions. The reaction order for quadruplex formation is 3 in 0.125 M KCl and 4 in LiCl solutions. The kinetics measurements suggest that quadruplex formation proceeds step by step via sequential strand association into duplex and triplex intermediate species. Triplex formation is rate limiting in 0.125 M KCl solution. In LiCl, each step of the association process depends on the strand concentration. Parallel reactions to formation of the fully matched canonical quadruplex may result in kinetically trapped mismatched quadruplexes making the canonical quadruplex practically inaccessible in particular at low temperature in KCl solution.
Figures





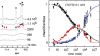

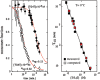
 , kof3 = 5.35 × 10−8 min−1 (corresponding to quadruplex lifetime of 35.6 years estimated by extrapolation at 0°C of the lifetimes displayed in Figure 7. kon3 = 105. The
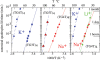
, kof3 = 5.35 × 10−8 min−1 (corresponding to quadruplex lifetime of 35.6 years estimated by extrapolation at 0°C of the lifetimes displayed in Figure 7. kon3 = 105. The  ratio accounting for the observed 3.2 reaction order is 10−5. The computed monomer equilibrium fractions correspond to a reduced dissociation constant, Fi = 6.2 × 10−7, in agreement with the measured value (Figure 4).
ratio accounting for the observed 3.2 reaction order is 10−5. The computed monomer equilibrium fractions correspond to a reduced dissociation constant, Fi = 6.2 × 10−7, in agreement with the measured value (Figure 4).References
-
- Gehring K, Leroy J.-L, Guéron M. A tetrameric DNA structure with protonated cytidine-cytidine base pairs. Nature. 1993;363:561–565. - PubMed
-
- Neidle S, Parkinson GN. The structure of telomeric DNA. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2003;13:275–283. - PubMed
-
- Davis JT. G-quartets 40 years later: from 5′-GMP to molecular biology and supramolecular chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2004;43:668–698. - PubMed
-
- Patel D, Bouaziz S, Kettani A, Wang Y. Structures of guanine-rich and cytosine rich quadruplexes formed by in vitro by telomeric, centromeric and triplets repeats desease DNA sequences. In: Neidel S, editor. Oxford Handbook of Nucleic Acid Structure. USA: Oxford University Press; 1999. pp. 390–452.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

