KNL1 and the CENP-H/I/K complex coordinately direct kinetochore assembly in vertebrates
- PMID: 18045986
- PMCID: PMC2230600
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e07-10-1051
KNL1 and the CENP-H/I/K complex coordinately direct kinetochore assembly in vertebrates
Abstract
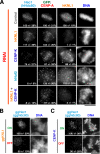
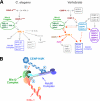
Chromosome segregation during mitosis requires the assembly of a large proteinaceous structure termed the kinetochore. In Caenorhabditis elegans, KNL-1 is required to target multiple outer kinetochore proteins. Here, we demonstrate that the vertebrate KNL1 counterpart is essential for chromosome segregation and is required to localize a subset of outer kinetochore proteins. However, unlike in C. elegans, depletion of vertebrate KNL1 does not abolish kinetochore localization of the microtubule-binding Ndc80 complex. Instead, we show that KNL1 and CENP-K, a subunit of a constitutively centromere-associated complex that is missing from C. elegans, coordinately direct Ndc80 complex localization. Simultaneously reducing both hKNL1 and CENP-K function abolishes all aspects of kinetochore assembly downstream of centromeric chromatin and causes catastrophic chromosome segregation defects. These findings explain discrepancies in kinetochore assembly pathways between different organisms and reveal a surprising plasticity in the assembly mechanism of an essential cell division organelle.
Figures



References
-
- Cheeseman I. M., Chappie J. S., Wilson-Kubalek E. M., Desai A. The conserved KMN network constitutes the core microtubule-binding site of the kinetochore. Cell. 2006;127:983–997. - PubMed
-
- DeLuca J. G., Gall W. E., Ciferri C., Cimini D., Musacchio A., Salmon E. D. Kinetochore microtubule dynamics and attachment stability are regulated by Hec1. Cell. 2006;127:969–982. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

