Massive but selective cytokine dysregulation in the colon of IL-10-/- mice revealed by multiplex analysis
- PMID: 18046045
- PMCID: PMC2756059
- DOI: 10.1093/intimm/dxm126
Massive but selective cytokine dysregulation in the colon of IL-10-/- mice revealed by multiplex analysis
Abstract
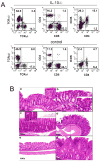
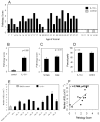
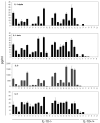
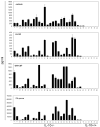
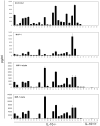
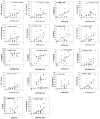
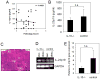
IL-10-deficient mice develop enterocolitis due to a failure of cytokine regulation; however, the full scope of that response remains poorly defined. Using multiplex analysis to quantify the activity of 23 regulatory and effector cytokines produced by colonic leukocytes, we demonstrate a vast dysregulation process of 18 cytokines in IL-10-/- mice from 7 to 27 weeks of age. Of those, IL-12p40, IL-6, granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor, IFN-gamma, IL-13 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) had the highest single correlations with pathology (r = 0.7766-0.7016). Importantly, there were strong associations (r = 0.7071-0.9074) between those cytokines and as many as 10 additional cytokines, indicating a high degree of cytokine complexity as disease progressed. IL-17 was notable in that it was produced at high levels by colonic leukocytes from IL-10-/- mice with pathology ranging from mild to severe, though it was not produced by healthy IL-10-/- mice lacking pathology. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) by itself displayed only a modest association with pathology (r = 0.6340), ranking sixth lowest, though it cross-correlated strongly with the synthesis of 12 other cytokines, implying that the destructive effects associated with TNFalpha may be due to interactions of multiple cytokine activities. IL-23 expression did not correlate with pathology, possibly suggesting that IL-23 is involved in the initiation but not the perpetuation of inflammation. Four cytokines (IL-2, IL-3, IL-4 and IL-5) remained negative in IL-10-/- mice, demonstrating that cytokine dysregulation was not universal. These findings emphasize the need to better understand cytokine networks in chronic inflammation and they provide a rationale for combining immunotherapies in the treatment of intestinal inflammation.
Figures


References
-
- Kuhn R, Lohler J, Rennick D, Rajewsky K, Muller W. Interleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic enterocolitis. Cell. 1993;75:263–74. - PubMed
-
- Mombaerts P, Mizoguchi E, Grusby MJ, Glimcher LH, Bhan AK, Tonegawa S. Spontaneous development of inflammatory bowel disease in T cell receptor mutant mice. Cell. 1993;75:274–82. - PubMed
-
- Moore KW, de Waal Malefyt R, Coffman RL, O'Garra A. Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:683–765. - PubMed
-
- Strober W, Fuss IJ, Blumberg RS. The immunology of mucosal models of inflammation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:495–549. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

