Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of oral testosterone enanthate plus dutasteride for 4 weeks in normal men: implications for male hormonal contraception
- PMID: 18046048
- PMCID: PMC2664381
- DOI: 10.2164/jandrol.107.004226
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of oral testosterone enanthate plus dutasteride for 4 weeks in normal men: implications for male hormonal contraception
Abstract
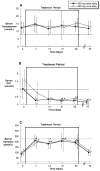
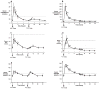
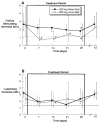
Oral administration of testosterone enanthate (TE) and dutasteride increases serum testosterone and might be useful for male hormonal contraception. To ascertain the contraceptive potential of oral TE and dutasteride by determining the degree of gonadotropin suppression mediated by 4 weeks of oral TE plus dutasteride, 20 healthy young men were randomly assigned to 4 weeks of either 400 mg oral TE twice daily or 800 mg oral TE once daily in a double-blinded, controlled fashion at a single site. All men received 0.5 mg dutasteride daily. Blood for measurement of serum luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), testosterone, dihydrotesterone (DHT), and estradiol was obtained prior to treatment, weekly during treatment, and 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 13, 14, 16, 20, and 24 hours after the morning dose on the last day of treatment. FSH was significantly suppressed throughout treatment with 800 mg TE once daily and after 4 weeks of treatment with 400 mg TE twice daily. LH was significantly suppressed after 2 weeks of treatment with 800 mg TE, but not with 400 mg TE. Serum DHT was suppressed and serum estradiol increased during treatment in both groups. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol was suppresed during treatment, but liver function tests, hematocrit, creatinine, mood, and sexual function were unaffected. The administration of 800 mg oral TE daily combined with dutasteride for 28 days significantly suppresses gonadotropins without untoward side effects and might have utility as part of a male hormonal contraceptive regimen.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison between testosterone enanthate-induced azoospermia and oligozoospermia in a male contraceptive study. I: Plasma luteinizing hormone, follicle stimulating hormone, testosterone, estradiol, and inhibin concentrations.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Jul;77(1):290-3. doi: 10.1210/jcem.77.1.8325955. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993. PMID: 8325955
-
Levonorgestrel implants (Norplant II) for male contraception clinical trials: combination with transdermal and injectable testosterone.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Aug;87(8):3562-72. doi: 10.1210/jcem.87.8.8710. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002. PMID: 12161475 Clinical Trial.
-
Low dose of cyproterone acetate and testosterone enanthate for contraception in men.Hum Reprod. 1998 May;13(5):1225-9. doi: 10.1093/humrep/13.5.1225. Hum Reprod. 1998. PMID: 9647551 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of chronic testosterone administration in normal men: safety and efficacy of high dosage testosterone and parallel dose-dependent suppression of luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, and sperm production.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Jan;70(1):282-7. doi: 10.1210/jcem-70-1-282. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990. PMID: 2104626 Clinical Trial.
-
Delivering non-hormonal contraceptives to men: advances and obstacles.Trends Biotechnol. 2008 Feb;26(2):90-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2007.10.009. Epub 2008 Jan 11. Trends Biotechnol. 2008. PMID: 18191256 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Steady-state pharmacokinetics of oral testosterone undecanoate with concomitant inhibition of 5α-reductase by finasteride.Int J Androl. 2011 Dec;34(6 Pt 1):541-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.2010.01120.x. Epub 2010 Oct 24. Int J Androl. 2011. PMID: 20969601 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Testosterone, HDL and cardiovascular risk in men: the jury is still out.Clin Lipidol. 2012 Aug 1;7(4):363-365. doi: 10.2217/clp.12.38. Clin Lipidol. 2012. PMID: 25379057 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogens and development of the rete testis, efferent ductules, epididymis and vas deferens.Differentiation. 2021 Mar-Apr;118:41-71. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2020.11.004. Epub 2020 Dec 13. Differentiation. 2021. PMID: 33441255 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amory JK, Bremner WJ. Oral testosterone in oil plus dutasteride: a pharmacokinetic study in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:2610–2617. - PubMed
-
- Amory JK, Page ST, Bremner WJ. Oral testosterone in oil: pharmacokinetic effects of 5α reduction with finasteride or dutasteride and food intake in men. J Androl. 2006;27:72–78. - PubMed
-
- Amory JK, Wang C, Swerdloff R, Anawalt BD, Matsumoto AM, Bremner WJ, Walker SE, Haberer LJ, Clark RV. The effect of 5α-reductase inhibition with dutasteride and finasteride on semen parameters and serum hormones in healthy men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:1659–1665. - PubMed
-
- Bagatell CJ, Bahl KD, Bremner WJ. The direct pituitary effect of testosterone to inhibit gonadotropin secretion in men is partially mediated by aromatization to estradiol. J Androl. 1994;15:15–21. - PubMed
-
- Bebb RA, Anawalt BD, Christensen RB, Paulsen CA, Bremner WJ, Matsumoto AM. Combined administration of levonorgestrel and testosterone induces more rapid and effective suppression of spermatogenesis than testosterone alone: a promising male contraceptive approach. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81:757–762. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

