Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of oral testosterone enanthate plus dutasteride for 4 weeks in normal men: implications for male hormonal contraception
- PMID: 18046048
- PMCID: PMC2664381
- DOI: 10.2164/jandrol.107.004226
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of oral testosterone enanthate plus dutasteride for 4 weeks in normal men: implications for male hormonal contraception
Abstract
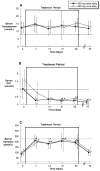
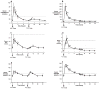
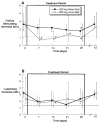
Oral administration of testosterone enanthate (TE) and dutasteride increases serum testosterone and might be useful for male hormonal contraception. To ascertain the contraceptive potential of oral TE and dutasteride by determining the degree of gonadotropin suppression mediated by 4 weeks of oral TE plus dutasteride, 20 healthy young men were randomly assigned to 4 weeks of either 400 mg oral TE twice daily or 800 mg oral TE once daily in a double-blinded, controlled fashion at a single site. All men received 0.5 mg dutasteride daily. Blood for measurement of serum luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), testosterone, dihydrotesterone (DHT), and estradiol was obtained prior to treatment, weekly during treatment, and 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 13, 14, 16, 20, and 24 hours after the morning dose on the last day of treatment. FSH was significantly suppressed throughout treatment with 800 mg TE once daily and after 4 weeks of treatment with 400 mg TE twice daily. LH was significantly suppressed after 2 weeks of treatment with 800 mg TE, but not with 400 mg TE. Serum DHT was suppressed and serum estradiol increased during treatment in both groups. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol was suppresed during treatment, but liver function tests, hematocrit, creatinine, mood, and sexual function were unaffected. The administration of 800 mg oral TE daily combined with dutasteride for 28 days significantly suppresses gonadotropins without untoward side effects and might have utility as part of a male hormonal contraceptive regimen.
Figures
References
-
- Amory JK, Bremner WJ. Oral testosterone in oil plus dutasteride: a pharmacokinetic study in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:2610–2617. - PubMed
-
- Amory JK, Page ST, Bremner WJ. Oral testosterone in oil: pharmacokinetic effects of 5α reduction with finasteride or dutasteride and food intake in men. J Androl. 2006;27:72–78. - PubMed
-
- Amory JK, Wang C, Swerdloff R, Anawalt BD, Matsumoto AM, Bremner WJ, Walker SE, Haberer LJ, Clark RV. The effect of 5α-reductase inhibition with dutasteride and finasteride on semen parameters and serum hormones in healthy men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:1659–1665. - PubMed
-
- Bagatell CJ, Bahl KD, Bremner WJ. The direct pituitary effect of testosterone to inhibit gonadotropin secretion in men is partially mediated by aromatization to estradiol. J Androl. 1994;15:15–21. - PubMed
-
- Bebb RA, Anawalt BD, Christensen RB, Paulsen CA, Bremner WJ, Matsumoto AM. Combined administration of levonorgestrel and testosterone induces more rapid and effective suppression of spermatogenesis than testosterone alone: a promising male contraceptive approach. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81:757–762. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

