Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce TAP, LMP, Tapasin genes and MHC class I antigen presentation by melanoma cells
- PMID: 18046553
- PMCID: PMC3146348
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-007-0402-4
Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce TAP, LMP, Tapasin genes and MHC class I antigen presentation by melanoma cells
Abstract
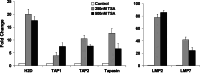
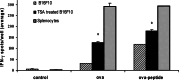
Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi), including trichostatin A (TSA) and valproic acid, can alter the acetylation of histones in chromatin and enhance gene transcription. Previously we demonstrated that HDACi-treated tumor cells are capable of presenting antigen via the MHC class II pathway. In this study, we show that treatment with HDACi enhances the expression of molecules (TAP1, TAP2, LMP2, LMP7, Tapasin and MHC class I) involved in antigen processing and presentation via the MHC class I pathway in melanoma cells. HDACi treatment of B16F10 cells also enhanced cell surface expression of class I and costimulatory molecules CD40 and CD86. Enhanced transcription of these genes is associated with a significant increase in direct presentation of whole protein antigen and MHC class I-restricted peptides by TSA-treated B16F10 cells. Our data indicate that epigenetic modification can convert a tumor cell to an antigen presenting cell capable of activating IFN-gamma secreting T cells via the class I pathway. These findings suggest that the abnormalities, observed in some tumors in the expression of MHC class I antigen processing and presentation molecules, may result from epigenetic repression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epigenetic enhancement of antigen processing and presentation promotes immune recognition of tumors.Cancer Res. 2008 Dec 1;68(23):9601-7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5270. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 19047136
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces coordinated changes in major histocompatibility class I presentation pathway, resulting in increased stability of class I complexes at the cell surface.Blood. 2001 Aug 15;98(4):1108-15. doi: 10.1182/blood.v98.4.1108. Blood. 2001. PMID: 11493458
-
Analysis of the MHC class I antigen presentation machinery in human embryonal carcinomas: evidence for deficiencies in TAP, LMP and MHC class I expression and their upregulation by IFN-gamma.Scand J Immunol. 1997 Dec;46(6):625-32. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3083.1997.d01-176.x. Scand J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9420627
-
Genes regulating MHC class I processing of antigen.Curr Opin Immunol. 1999 Feb;11(1):82-8. doi: 10.1016/s0952-7915(99)80015-6. Curr Opin Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10047538 Review.
-
Antigen processing by the class I pathway.Biochem Soc Trans. 1995 Aug;23(3):664-9. doi: 10.1042/bst0230664. Biochem Soc Trans. 1995. PMID: 8566439 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Understanding the Impact of ErbB Activating Events and Signal Transduction on Antigen Processing and Presentation: MHC Expression as a Model.Front Pharmacol. 2016 Sep 26;7:327. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00327. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27729860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combining cancer immunotherapy and targeted therapy.Curr Opin Immunol. 2013 Apr;25(2):291-6. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2013.02.011. Epub 2013 Apr 2. Curr Opin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23561594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA Methyltransferase Inhibitors: Catalysts For Antitumour Immune Responses.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Dec 12;12:10903-10916. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S217767. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31849494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Perspective of Immunotherapy for Cancers.Cells. 2023 Jan 19;12(3):365. doi: 10.3390/cells12030365. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36766706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overcoming Barriers in Oncolytic Virotherapy with HDAC Inhibitors and Immune Checkpoint Blockade.Viruses. 2016 Jan 6;8(1):9. doi: 10.3390/v8010009. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 26751469 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Armeanu S, Bitzer M, Lauer UM, Venturelli S, Pathil A, Krusch M, Kaiser S, Jobst J, Smirnow I, Wagner A, Steinle A, Salih HR. Natural killer cell-mediated lysis of hepatoma cells via specific induction of NKG2D ligands by the histone deacetylase inhibitor sodium valproate. Cancer Res. 2005;65:6321–6329. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4252. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chang C-C, Ogino T, Mullins DW, Oliver JL, Yamshchikov GV, Bandoh N, Slingluff CL, Jr, Ferrone S. Defective human leukocyte antigen class I-associated antigen presentation caused by a novel beta2-microglobulin loss-of-function in melanoma cells. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:18763–18773. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M511525200. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

