Nucleolus: the fascinating nuclear body
- PMID: 18046571
- PMCID: PMC2137947
- DOI: 10.1007/s00418-007-0359-6
Nucleolus: the fascinating nuclear body
Abstract
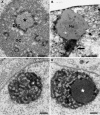
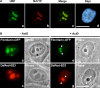
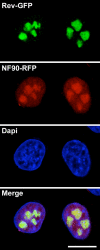
Nucleoli are the prominent contrasted structures of the cell nucleus. In the nucleolus, ribosomal RNAs are synthesized, processed and assembled with ribosomal proteins. RNA polymerase I synthesizes the ribosomal RNAs and this activity is cell cycle regulated. The nucleolus reveals the functional organization of the nucleus in which the compartmentation of the different steps of ribosome biogenesis is observed whereas the nucleolar machineries are in permanent exchange with the nucleoplasm and other nuclear bodies. After mitosis, nucleolar assembly is a time and space regulated process controlled by the cell cycle. In addition, by generating a large volume in the nucleus with apparently no RNA polymerase II activity, the nucleolus creates a domain of retention/sequestration of molecules normally active outside the nucleolus. Viruses interact with the nucleolus and recruit nucleolar proteins to facilitate virus replication. The nucleolus is also a sensor of stress due to the redistribution of the ribosomal proteins in the nucleoplasm by nucleolus disruption. The nucleolus plays several crucial functions in the nucleus: in addition to its function as ribosome factory of the cells it is a multifunctional nuclear domain, and nucleolar activity is linked with several pathologies. Perspectives on the evolution of this research area are proposed.
Figures
References
-
- Andersen JS, Lyon CE, Fox AH, Leung AKL, Lam YW, Steen H, Mann M, Lamond AI (2002) Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus. Curr Biol 12:1–11 - PubMed
-
- Andersen JS, Lam YW, Leung AK, Ong SE, Lyon CE, Lamond AI, Mann M (2005) Nucleolar proteome dynamics. Nature 433:77–83 - PubMed
-
- Arabi A, Wu S, Ridderstrale K, Bierhoff H, Shiue C, Fatyol K, Fahlen S, Hydbring P, Soderberg O, Grummt I et al (2005) c-Myc associates with ribosomal DNA and activates RNA polymerase I transcription. Nat Cell Biol 7:303–310 - PubMed
-
- Azum-Gélade M-C, Noaillac-Depeyre J, Caizergues-Ferrer M, Gas N (1994) Cell cycle redistribution of U3 snRNA and fibrillarin. Presence in the cytoplasmic nucleolus remnant and in the prenucleolar bodies at telophase. J Cell Sci 107:463–475 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

