Use of Respimat Soft Mist inhaler in COPD patients
- PMID: 18046862
- PMCID: PMC2707154
- DOI: 10.2147/copd.2006.1.3.251
Use of Respimat Soft Mist inhaler in COPD patients
Abstract
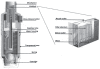
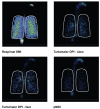
Events of the past decade have stimulated development of new drug formulations and delivery devices that have improved the efficiency, ease of use, and environmental impact of inhaled drug therapy. Respimat Soft Mist Inhaler is a novel, multidose, propellant-free, hand-held, liquid inhaler that represents a new category of inhaler devices. The aerosol cloud generated by Respimat contains a higher fraction of fine particles than most pressurized metered dose inhalers (pMDIs) and dry powder inhalers (DPIs), and the aerosol spray exits the inhaler more slowly and for a longer duration than with pMDIs. This translates into higher lung drug deposition and lower oropharyngeal deposition, making it possible to give lower nominal doses of delivered drugs without lowering efficacy. In clinical trials in patients with COPD, bronchodilator drugs delivered from Respimat were equally effective at half of the dose delivered from a pMDI. In one study of inhaler preference, Respimat was preferred over the pMDI by patients with COPD and other obstructive lung diseases. Respimat is a valuable addition to the range of inhaler devices available to the patient with COPD.
Figures



References
-
- Dalby R, Spallek M, Voshaar T. A review of the development of Respimat® Soft Mist Inhaler™. Int J Pharm. 2004;283:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Dolovich MB, Ahrens RC, Hess DR, et al. Device selection and outcomes of aerosol therapy: evidence-based guidelines. Chest. 2005;127:335–71. - PubMed
-
- Fink JB. Metered-dose inhalers, dry powder inhalers, and transitions. Resp Care. 2000;45:623–35. - PubMed
-
- Fink JB, Rubin BK. Problems with inhaler use: a call for improved clinician and patient education. Respir Care. 2005;50:1360–74. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg J, Freund E, Beckers B, et al. Improved delivery of fenoterol plus ipratropium bromide using Respimat® compared with a conventional metered dose inhaler. Eur Respir J. 2001;17:225–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

