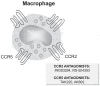
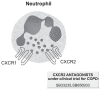
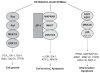
Biological targets for therapeutic interventions in COPD: clinical potential
- PMID: 18046869
- PMCID: PMC2707155
- DOI: 10.2147/copd.2006.1.3.321
Biological targets for therapeutic interventions in COPD: clinical potential
Abstract
COPD is a widespread inflammatory respiratory disorder characterized by a progressive, poorly reversible airflow limitation. Currently available therapies are mostly based on those used to treat asthma. However, such compounds are not able to effectively reduce the gradual functional deterioration, as well as the ongoing airway and lung inflammation occurring in COPD patients. Therefore, there is an urgent need to improve the efficacy of the existing drug classes and to develop new treatments, targeting the main cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying disease pathogenesis. These therapeutic strategies will be highlighted in the present review.
Figures
References
-
- Adams RH, Porras A, Alonso G, et al. Essential role of p38α MAP kinase in placental but not embryonic cardiovascular development. Mol Cell. 2000;6:109–16. - PubMed
-
- Alabaster VA. Discovery and development of selective M3 antagonists for clinical use. Life Sci. 1997;60:1053–60. - PubMed
-
- Antonicelli F, Brown D, Parmentier M, et al. Regulation of LPS-mediated inflammation in vivo and in vitro by the thiol antioxidant nacystelyn. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2004;286:L1319–27. - PubMed
-
- Asadullah K, Sterry W, Volk HD. Interleukin-10 therapy – review of a new approach. Pharmacol Rev. 2003;55:241–69. - PubMed
-
- Ayala JM, Goyal S, Liverton NJ, et al. Serum-induced monocyte differentiation and monocyte chemotaxis are regulated by the p38 MAP kinase signal transduction pathway. J Leukoc Biol. 2000;67:869–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical