Evidence of Parelaphostrongylus tenuis infections in free-ranging elk (Cervus elaphus) in southern Ontario
- PMID: 18050795
- PMCID: PMC2034421
Evidence of Parelaphostrongylus tenuis infections in free-ranging elk (Cervus elaphus) in southern Ontario
Abstract
The antemortem detection of a Parelaphostrongylus tenuis infection in a free-ranging wild elk (Cervus elaphus) in southern Ontario is documented. Postmortems on other free-ranging elk that died during 2000-2005 indicated that 59% (17/29) were infected with P. tenuis, based on presence of lesions in the brain.
Preuves d’infections à Parelaphostrongylus tenuis chez le wapiti (Cervus elaphus) en élevage extensif dans le sud de l’Ontario. Cet article décrit la détection antémortem d’une infection à Parelaphostrongylus tenuis chez un wapiti en élevage extensif (Cervus elaphus) dans le sud de l’Ontario. Des examens post mortem réalisés sur d’autres wapitis en élevage extensif, morts entre 2000 et 2005, ont révélé que 59 % (17/29) présentaient des lésions au cerveau caractéristiques d’infection à P. tenuis.
(Traduit par Docteur André Blouin)
Figures

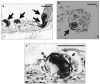
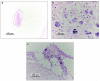
References
-
- Rosatte RC, Hamr J, Ranta B, Young J, Cool N. Elk restoration in Ontario, Canada: Infectious disease management strategy, 1998–2001. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2002;969:358–363. - PubMed
-
- Pybus M, Samuel W, Crichton V. Identification of dorsal spined larvae from free-ranging wapiti (Cervus elaphus) in southwestern Manitoba. J Wildl Dis. 1989;25:291–293. - PubMed
-
- Forrester S, Lankester M. Extracting protostrongylid nematode larvae from ungulate feces. J Wildl Dis. 1997;33:511–516. - PubMed
-
- Anderson RC, Lankester MW, Strelive UR. Further experimental studies of Pneumostrongylus tenuis in cervids. Can J Zool. 1966;41:851–861. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
