The glucocorticoid receptor signalling in breast cancer
- PMID: 18053085
- PMCID: PMC3823477
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00177.x
The glucocorticoid receptor signalling in breast cancer
Abstract
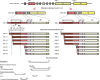
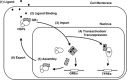
Glucocorticoids are provided as co-medication with chemotherapy in breast cancer, albeit several lines of evidence indicate that their use may have diverse effects and in fact may inhibit chemosensitivity. The molecular basis of glucocorticoid-induced resistance to chemotherapy in breast cancer remains poorly defined. Recent researchers, in an attempt to clarify some aspects of the underlying pathways, provide convincing evidence that glucocorticoids induce effects that are dependent upon the glucocorticoid receptor -mediated transcriptional regulation of specific genes known to play key roles in cellular/tissue functions, including growth, apoptosis, differentiation, metastasis and cell survival. In this review, we focus on how glucocorticoid-induced chemoresistance in breast cancer is mediated by the glucocorticoid receptor, unraveling the molecular interplay of glucocorticoid receptor signaling with other signaling cascades prevalent in breast cancer. We also include a detailed description of glucocorticoid receptor structure and function, summarizing data gained during recent years into the mechanism(s) of the cross-talk between the glucocorticoid receptor and other signaling cascades and secondary messengers, via which glucocorticoids exert their pleiotropic effects.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Murray T, Samuels A, Ghafoor A, Ward E, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2003. CA Cancer J. Clin. 53:5–26. - PubMed
-
- Carter CL, Allen C, Henson DE. Relation of tumor size, lymph node status and survival in 24,740 breast cancer cases. Cancer. 1989;63:181–7. - PubMed
-
- Herr I, Gassler N, Friess H, Büchler MW. Regulation of differential pro- and anti-apoptotic signaling by glucocorticoids. Apoptosis. 2007;12:271–91. - PubMed
-
- Grote T, Hajdenberg J, Cartmell A, Ferguson S, Ginkel A, Charu V. Combination therapy for chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in patients receiving moderately emetogenic chemotherapy: palonoseetron, dexamethasone and aprepitant. J Support Oncol. 2006;4:403–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

