Acidic pre-conditioning suppresses apoptosis and increases expression of Bcl-xL in coronary endothelial cells under simulated ischaemia
- PMID: 18053090
- PMCID: PMC3918074
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00172.x
Acidic pre-conditioning suppresses apoptosis and increases expression of Bcl-xL in coronary endothelial cells under simulated ischaemia
Abstract
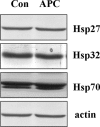
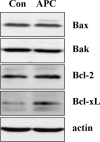
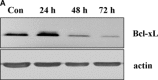
Ischaemic pre-conditioning has a powerful protective potential against ischaemia-induced cell death, and acidosis is an important feature of ischaemia and can lead to apoptosis. Here we tested whether pre-conditioning with acidosis, that is, acidic pre-conditioning (APC), may protect coronary endothelial cells (EC) against apoptosis induced by simulated ischaemia. For pre-conditioning, EC were exposed fo 40 min. to acidosis (pH 6.4) followed by a 14-hrs recovery period (pH 7.4) and finally treated for 2 hrs with simulated ischaemia (glucose-free anoxia at pH 6.4). Cells undergoing apoptosis were visualized by chromatin staining or by determination of caspase-3 activity Simulated ischaemia in untreated EC increased caspase-3 activity and the number of apoptotic cell (31.3 +/- 1.3%versus 3.9 +/- 0.6% in control). APC significantly reduced the rate of apoptosis (14.2 +/- 1.3%) and caspase-3 activity. Western blot analysis exploring the under lying mechanism leading to this protection revealed suppression of the endoplasmic reticulum- (reduced cleavage of caspase-12) and mitochondria-mediated (reduced cytochrome C release) pathways of apoptosis. These effects were associated with an over-expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-xL 14 hrs after APC, whereas no effect on the expression of Bcl-2, Bax, Bak, procaspase-12, reticulum-localized chaperones (GRP78, calreticulin), HSP70, HSP32 and HSP27 could be detected. Knock-down of Bcl-xL by siRNA-treatment prevented the protective effect of APC. In conclusion, short acidic pre-treatment can protect EC against ischaemic apoptosis. The mechanism of this protection consists of suppression of the endoplasmic reticulum- and mitochondria-mediated pathways. Over-expression of the anti apoptotic protein Bcl-xL is responsible for the increased resistance to apoptosis during ischaemic insult.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Importance of bicarbonate transport for ischaemia-induced apoptosis of coronary endothelial cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2007 Jul-Aug;11(4):798-809. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00053.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2007. PMID: 17760841 Free PMC article.
-
Acidic preconditioning protects endothelial cells against apoptosis through p38- and Akt-dependent Bcl-xL overexpression.Apoptosis. 2009 Jan;14(1):90-6. doi: 10.1007/s10495-008-0287-5. Apoptosis. 2009. PMID: 19082728 Free PMC article.
-
Ischemic acidosis causes apoptosis in coronary endothelial cells through activation of caspase-12.Cardiovasc Res. 2007 Jan 1;73(1):172-80. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.09.018. Epub 2006 Sep 29. Cardiovasc Res. 2007. PMID: 17083921
-
[Overcoming acquired resistance to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand by Bcl-XL small interfering RNA in human colon cancer].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2008 Apr;30(4):245-9. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 18788624 Chinese.
-
Mollugin induces apoptosis in human Jurkat T cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated activation of JNK and caspase-12 and subsequent activation of mitochondria-dependent caspase cascade regulated by Bcl-xL.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009 Dec 1;241(2):210-20. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2009.08.024. Epub 2009 Aug 28. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19716835
Cited by
-
Responses of Endothelial Cells Towards Ischemic Conditioning Following Acute Myocardial Infarction.Cond Med. 2018 Aug;1(5):247-258. Cond Med. 2018. PMID: 30338315 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular pH Regulates TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis and Necroptosis in Endothelial Cells.J Immunol Res. 2017;2017:1503960. doi: 10.1155/2017/1503960. Epub 2017 Aug 13. J Immunol Res. 2017. PMID: 28884134 Free PMC article.
-
Ex vivo acidic preconditioning enhances bone marrow ckit+ cell therapeutic potential via increased CXCR4 expression.Eur Heart J. 2013 Jul;34(26):2007-16. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehr219. Epub 2011 Jul 22. Eur Heart J. 2013. PMID: 21784762 Free PMC article.
-
Acidic stress induces apoptosis and inhibits angiogenesis in human bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells.Oncol Lett. 2017 Nov;14(5):5695-5702. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6947. Epub 2017 Sep 15. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 29113197 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and molecular mechanisms of endothelial ischemia/reperfusion injury: perspectives and implications for postischemic myocardial protection.Am J Transl Res. 2016 Feb 15;8(2):765-77. eCollection 2016. Am J Transl Res. 2016. PMID: 27158368 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Scarabelli T, Stephanou A, Rayment N, Pasini E, Comini L, Curello S, Ferrari R, Knight R, Latchman D. Apoptosis of endothelial cells precedes myocyte cell apoptosis in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circulation. 2001;104:253. - PubMed
-
- Werner N, Wassmann S, Ahlers P, Kosiol S, Nickenig G. Circulating CD31+/annexin V+ apoptotic microparticles correlate with coronary endothelial function in patients with coronary artery disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:112. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Mehta JL, Haider N, Zhang X, Narula J, Li D. Role of caspases in Ox-LDL-induced apoptotic cascade in human coronary artery endothelial cells. Circ Res. 2004;94:370. - PubMed
-
- Bombeli T, Karsan A, Tait JF, Harlan JM. Apoptotic vascular endothelial cells become procoagulant. Blood. 1997;89:2429–442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

