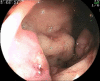
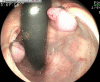
Hematochezia in a patient with liver cirrhosis
- PMID: 18053218
- PMCID: PMC2213638
- DOI: 10.1186/1749-7922-2-32
Hematochezia in a patient with liver cirrhosis
Abstract
Although commonly detectable in patients with cirrhosis, rectal varices only infrequently cause significant hematochezia (0.5-3.6%). While they may be expected to resolve with treatment of the concomitant portal hypertension, there is currently no standardized approach to their management in isolation. Therefore many authorities recommend transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting (TIPS) as a means of alleviating otherwise recalcitrant bleeding. Conceptually, however, rectal varices should be as amenable to local therapies as are their counterparts occurring at the esophagogastric junction. In this report, we describe the use of endoscopic banding per ano to alleviate significant rectal bleeding in a patient with poorly controlled portal hypertension. This allowed medical optimisation so that the underlying pathology could be controlled without recourse to TIPS or other means of creating a formal portosystemic shunt.
Figures
References
-
- Nayar M, Saravanan R, Rowlands PC, McWilliams RG, Evans J, Sutton RJ, Gilmore IT, Smart HL, Lombard MG. TIPSS in the treatment of ectopic variceal bleeding. Hepatogastroenterology. 2006;53:584–587. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources