Transcriptional regulation of Th17 cell differentiation
- PMID: 18053739
- PMCID: PMC2696342
- DOI: 10.1016/j.smim.2007.10.011
Transcriptional regulation of Th17 cell differentiation
Abstract
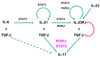
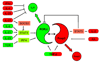
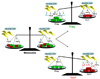
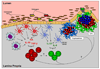
The paradigm of effector T helper cell differentiation into either Th1 or Th2 lineages has been profoundly shaken by the discovery of T cells that secrete IL-17 and other inflammatory cytokines. This subset, referred to as Th17, is centrally involved in autoimmune disease and is important in host defense at mucosal surfaces. In mouse, a series of cytokines, including IL-6, IL-21, IL-23, and TGF-beta, function sequentially or synergistically to induce the Th17 lineage. Other cytokines, including IL-2, IL-4, IFNgamma, and IL-27, inhibit differentiation of this lineage. Here we review how the nuclear orphan receptor RORgammat functions to coordinate the diverse cytokine-induced signals and thus controls Th17 cell differentiation.
Figures
References
-
- Mosmann TR, Coffman RL. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–173. - PubMed
-
- Cua DJ, Sherlock J, Chen Y, Murphy CA, Joyce B, Seymour B, et al. Interleukin-23 rather than interleukin-12 is the critical cytokine for autoimmune inflammation of the brain. Nature. 2003;421:744–748. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

