Neutralization of two North American coral snake venoms with United States and Mexican antivenoms
- PMID: 18054059
- PMCID: PMC3293456
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2007.10.004
Neutralization of two North American coral snake venoms with United States and Mexican antivenoms
Abstract
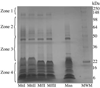
Elapid snakes throughout the world are considered very lethal, containing neurotoxic venoms that affect the nervous system. When humans are envenomated it is considered a serious medical emergency, and antivenom is the main form of treatment considered, in spite of the fact that some patients may only survive under intensive therapy treatment such as respiratory support. Coral snakes are part of the family Elapidae and envenomations by these snakes are very low (<2% of total snakebites) in most countries from southeastern United States to Argentina. In the United States, there are only two species of coral snakes of medical importance that belong to the Micrurus genera: Micrurus fulvius fulvius (Eastern coral snake) and Micrurus tener tener (Texas coral snake). In 2006, Wyeth pharmaceutical notified customers that the production of the North American coral snake antivenin (NACSA) in the US was discontinued and adequate supplies were available to meet historical needs through the end of October 2008; and therefore, it is of utmost important to consider other antivenoms as alternatives for the treatment of coral snake envenoming. One logical alternative is the coral snake antivenom, Coralmyn, produced by the Mexican company, Bioclon. In order to compare neutralization between NACSA and Coralmyn antivenoms with the North American coral snake venoms, the venom lethal doses (LD(50)) and antivenom effective doses (ED(50)) were determined in 18-20 g, female, BALB/c mice. Additionally, venom comparisons were determined through a non-reduced SDS-PAGE for M.f.fulvius, M.t.tener and the Mexican coral snake venom, Micrurus nigrocinctus nigrocinctus. Coralmyn antivenom was able to effectively neutralize three LD(50) doses of all venom from both M.t.tener and M.f.fulvius, while Wyeth antivenom only neutralized M.f.fulvius venom and was not effective in neutralizing three LD(50) doses of M.t.tener venom. Coralmyn is effective in the neutralization of both clinically important coral snake venoms in the US.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Australian tiger snake (Notechis scutatus) and mexican coral snake (Micruris species) antivenoms prevent death from United States coral snake (Micrurus fulvius fulvius) venom in a mouse model.J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 2003;41(1):7-10. doi: 10.1081/clt-120018264. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 2003. PMID: 12645961
-
Cross neutralization of coral snake venoms by commercial Australian snake antivenoms.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2017 Jan;55(1):33-39. doi: 10.1080/15563650.2016.1222615. Epub 2016 Sep 5. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2017. PMID: 27595162
-
The Bold and the Beautiful: a Neurotoxicity Comparison of New World Coral Snakes in the Micruroides and Micrurus Genera and Relative Neutralization by Antivenom.Neurotox Res. 2017 Oct;32(3):487-495. doi: 10.1007/s12640-017-9771-4. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Neurotox Res. 2017. PMID: 28674788
-
Coral snake bites (Micrurus spp.) in Brazil: a review of literature reports.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2016 Mar;54(3):222-34. doi: 10.3109/15563650.2015.1135337. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2016. PMID: 26808120 Review.
-
A Quest for a Universal Plasma-Derived Antivenom Against All Elapid Neurotoxic Snake Venoms.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 23;12:668328. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.668328. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33968072 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo neutralization of coral snake venoms with an oligoclonal nanobody mixture in a murine challenge model.Nat Commun. 2024 May 21;15(1):4310. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48539-z. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38773068 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological Cross-Reactivity and Preclinical Assessment of a Colombian Anticoral Antivenom against the Venoms of Three Micrurus Species.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Feb 15;16(2):104. doi: 10.3390/toxins16020104. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38393182 Free PMC article.
-
First reported case of African Viper bite treated with Indian Polyvalent Anti Snake Venom.Med J Armed Forces India. 2010 Apr;66(2):199-200. doi: 10.1016/S0377-1237(10)80154-6. Epub 2011 Jul 21. Med J Armed Forces India. 2010. PMID: 27375340 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A polyvalent coral snake antivenom with broad neutralization capacity.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Mar 11;13(3):e0007250. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007250. eCollection 2019 Mar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 30856180 Free PMC article.
-
Coral snake antivenom produced in chickens (Gallus domesticus).Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2014 Jan-Feb;56(1):61-6. doi: 10.1590/S0036-46652014000100009. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2014. PMID: 24553610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aird SD, da Silva NJ. Comparative enzymatic composition of Brazilian coral snake (Micrurus) venoms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B. 1991;99:287–294. - PubMed
-
- Alape-Giron A, Stiles B, Schmidt J, Giron-Cortés M, Thelestam M, Jornvall H, Bergman T. Characterization of multiple nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-binding protiens and phospholipases A2 from the venom of the coral snake Micrurus nigrocinctus. FEBS Lett. 1996;380:29–32. - PubMed
-
- Amuy E, Alape-Girón A, Lomonte B, Thelestam M, Gutiérrez JM. Development of immunoassays for determination of circulating venom antigens during envenomations by coral snakes (Micrurus species) Toxicon. 1997;35:1605–1616. - PubMed
-
- Arce V, Rojas E, Ownby CL, Rojas G, Gutiérrez JM. Preclinical assessment of the ability of polyvalent (Crotalinae) and anticoral (Elapidae) antivenoms produced in Costa Rica to neutralize the venoms of North American snakes. Toxicon. 2003;41:851–860. - PubMed
-
- Borys DJ, Tobleman WR, Standford RD, Morgan DL. Is antivenin required for all Texas coral snake (Micrurus fulvius tenere) envenomation? Abstract: Clinical Toxicology. 2005;43:709.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

