Surface-displayed porcine epidemic diarrhea viral (PEDV) antigens on lactic acid bacteria
- PMID: 18054413
- PMCID: PMC7115547
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.10.065
Surface-displayed porcine epidemic diarrhea viral (PEDV) antigens on lactic acid bacteria
Abstract
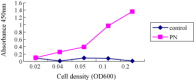
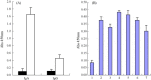
In this report, for surface display of viral antigen on lactobacilli, we have developed a surface antigen display system using the poly-gamma-glutamate synthetase A protein (pgsA) of Bacillus subtilis as an anchoring matrix. Recombinant fusion proteins comprised of pgsA and neucleocapsid protein of PEDV were stably expressed in Lactobacillus casei. Surface location of fusion protein was verified by ELISA, immunofluoresence microscopy. Oral and intranasal inoculations of recombinant L. casei into pregnant sow and mice resulted in high levels of serum immunoglobuline G (IgG) and mucosal IgA, as demonstrated by rnELISA(recombinant N protein ELISA) using recombinant N protein. Absorbance of IgG in pregnant sow sera highly increased duration of the experiment. More importantly, the level of IgA in colostrum were increased significantly higher than that of IgG. The IgG levels of the piglets were increased after suckling colostrum secreted from sows previously inoculated recombinant L. casei. These results indicate that mucosal immunization with recombinant L. casei expressing PEDV N protein (neucleoprotein of PEDV) on its surface elicited high levels of mucosal IgA and circulation IgG immune responses against the antigen N of PEDV.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Oral Immunization against PEDV with Recombinant Lactobacillus casei Expressing Dendritic Cell-Targeting Peptide Fusing COE Protein of PEDV in Piglets.Viruses. 2018 Mar 1;10(3):106. doi: 10.3390/v10030106. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 29494530 Free PMC article.
-
Mucosal immunization with surface-displayed severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein on Lactobacillus casei induces neutralizing antibodies in mice.J Virol. 2006 Apr;80(8):4079-87. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.8.4079-4087.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16571824 Free PMC article.
-
[Induction of immune response after oral inoculation of mice with Lactobacillus casei surface-displayed porcine epidemic diarrhea viral N protein].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2009 Jun;25(6):813-8. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2009. PMID: 19777806 Chinese.
-
S1 domain of the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus spike protein as a vaccine antigen.Virol J. 2016 Apr 1;13:57. doi: 10.1186/s12985-016-0512-8. Virol J. 2016. PMID: 27036203 Free PMC article.
-
Status of vaccines for porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in the United States and Canada.Virus Res. 2016 Dec 2;226:108-116. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.08.005. Epub 2016 Aug 18. Virus Res. 2016. PMID: 27545066 Review.
Cited by
-
Porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus: a comprehensive review of molecular epidemiology, diagnosis, and vaccines.Virus Genes. 2012 Apr;44(2):167-75. doi: 10.1007/s11262-012-0713-1. Epub 2012 Jan 22. Virus Genes. 2012. PMID: 22270324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-TGEV Miller Strain Infection Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum Supernatant Based on the JAK-STAT1 Signaling Pathway.Front Microbiol. 2019 Nov 6;10:2540. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02540. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31781061 Free PMC article.
-
Porcine epidemic diarrhea (PED) infection, diagnosis and vaccination: A mini review.Toxicol Environ Health Sci. 2016;8(5):277-289. doi: 10.1007/s13530-016-0287-8. Epub 2017 Jan 4. Toxicol Environ Health Sci. 2016. PMID: 32226596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against porcine epidemic diarrhea virus S1/S2 junction protein.AMB Express. 2023 Jul 12;13(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s13568-023-01573-4. AMB Express. 2023. PMID: 37436550 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of expression vectors in Lactobacillus reuteri strains.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2010 Jul 1;308(1):8-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2010.01978.x. Epub 2010 Apr 8. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2010. PMID: 20455948 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shaw D.M., Gaerthé B., Leer R.J., Van Der Stap J.G., Smittenaar C., Heijne Den Bak-Glashouwer M.-J. Engineering the microflora to vaccinate the mucosa: serum immunoglobulin G responses and activated draining cervical lymph nodes following mucosal application of tetanus toxin fragment C-expressing lactobacilli. Immunology. 2000;100(4):510–518. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Enjuanes L., Van der Zeijst B.A.M. Molecular basis of transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus (TGEV) epidemiology. In: Siddell S.G., editor. Coronavirus. Plenum; New York, NY: 1995. pp. 337–376.
-
- Ashiuchi M., Nawa C., Kamei T., Song J.J., Hong S.P., Sung M.H. Physiological and biochemical characteristics of poly gamma-glutamate synthetase complex of Bacillus subtilis. Eur J Biochem. 2001;268(20):5321–5328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

