Development and characterization of a standardized ELISA including a reference serum on each plate to detect antibodies induced by experimental malaria vaccines
- PMID: 18054414
- PMCID: PMC2253722
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.10.064
Development and characterization of a standardized ELISA including a reference serum on each plate to detect antibodies induced by experimental malaria vaccines
Abstract
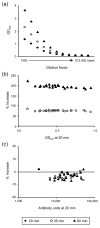
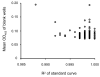
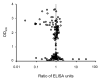
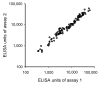
Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) has been widely used to measure antibody titers for evaluating the immunogenicity of a vaccine. However, there is as yet no generally accepted way of expressing the ELISA results in the case of experimental vaccines, since there is usually no uniform standard. Both end point and single dilution methods have significant disadvantages. In this paper, we obtained reproducible data with fewer dilutions of samples by addition of serially diluted standard serum to each ELISA plate. Since this ELISA method gives reliable antibody titer with less labor than other methods, it can strongly support vaccine development.
Figures


References
-
- Engvall E, Perlman P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G Immunochemistry. 1971;8(9):871–4. - PubMed
-
- Van Weemen BK, Schuurs AH. Immunoassay using antigen-enzyme conjugates. FEBS Lett. 1971;15(3):232–236. - PubMed
-
- Gheesling LL, Carlone GM, Pais LB, Holder PF, Maslanka SE, Plikaytis BD, et al. Multicenter comparison of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup C anti-capsular polysaccharide antibody levels measured by a standardized enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1994;32(6):1475–82. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Player VA, White D. Comparison of an ELISA system for the quantification of hepatitis B antibody with an automated and a semi-automated system. J Virol Methods. 1993;45(1):67–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

