Bloom's syndrome helicase and Mus81 are required to induce transient double-strand DNA breaks in response to DNA replication stress
- PMID: 18054789
- PMCID: PMC2276852
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.11.006
Bloom's syndrome helicase and Mus81 are required to induce transient double-strand DNA breaks in response to DNA replication stress
Abstract
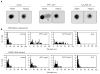
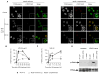
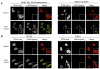
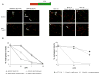
Perturbed DNA replication either activates a cell cycle checkpoint, which halts DNA replication, or decreases the rate of DNA synthesis without activating a checkpoint. Here we report that at low doses, replication inhibitors did not activate a cell cycle checkpoint, but they did activate a process that required functional Bloom's syndrome-associated (BLM) helicase, Mus81 nuclease and ataxia telangiectasia mutated and Rad3-related (ATR) kinase to induce transient double-stranded DNA breaks. The induction of transient DNA breaks was accompanied by dissociation of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) and DNA polymerase alpha from replication forks. In cells with functional BLM, Mus81 and ATR, the transient breaks were promptly repaired and DNA continued to replicate at a slow pace in the presence of replication inhibitors. In cells that lacked BLM, Mus81, or ATR, transient breaks did not form, DNA replication did not resume, and exposure to low doses of replication inhibitors was toxic. These observations suggest that BLM helicase, ATR kinase, and Mus81 nuclease are required to convert perturbed replication forks to DNA breaks when cells encounter conditions that decelerate DNA replication, thereby leading to the rapid repair of those breaks and resumption of DNA replication without incurring DNA damage and without activating a cell cycle checkpoint.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation of BLM, dissociation from topoisomerase IIIalpha, and colocalization with gamma-H2AX after topoisomerase I-induced replication damage.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Oct;25(20):8925-37. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.20.8925-8937.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16199871 Free PMC article.
-
Cleavage of stalled forks by fission yeast Mus81/Eme1 in absence of DNA replication checkpoint.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Feb;19(2):445-56. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-07-0728. Epub 2007 Nov 21. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18032583 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous gamma-H2AX-ATM-Chk2 checkpoint activation in Bloom's syndrome helicase deficient cells is related to DNA replication arrested forks.Mol Cancer Res. 2007 Jul;5(7):713-24. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-07-0028. Mol Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17634426
-
Role of the BLM helicase in replication fork management.DNA Repair (Amst). 2007 Jul 1;6(7):936-44. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2007.02.007. Epub 2007 Mar 23. DNA Repair (Amst). 2007. PMID: 17363339 Review.
-
Functions of RecQ family helicases: possible involvement of Bloom's and Werner's syndrome gene products in guarding genome integrity during DNA replication.J Biochem. 2001 Apr;129(4):501-7. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a002883. J Biochem. 2001. PMID: 11275547 Review.
Cited by
-
A replicator-specific binding protein essential for site-specific initiation of DNA replication in mammalian cells.Nat Commun. 2016 Jun 8;7:11748. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11748. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27272143 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-PKcs plays a dominant role in the regulation of H2AX phosphorylation in response to DNA damage and cell cycle progression.BMC Mol Biol. 2010 Mar 6;11:18. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-11-18. BMC Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20205745 Free PMC article.
-
The Mus81-Mms4 structure-selective endonuclease requires nicked DNA junctions to undergo conformational changes and bend its DNA substrates for cleavage.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jun;42(10):6511-22. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku265. Epub 2014 Apr 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24744239 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Deformation Causes DNA Damage by Increasing Replication Stress.Curr Biol. 2021 Feb 22;31(4):753-765.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.11.037. Epub 2020 Dec 15. Curr Biol. 2021. PMID: 33326770 Free PMC article.
-
A Link between Replicative Stress, Lamin Proteins, and Inflammation.Genes (Basel). 2021 Apr 9;12(4):552. doi: 10.3390/genes12040552. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33918867 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hickson ID. RecQ helicases: caretakers of the genome. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:169–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

