Inhibition and brain work
- PMID: 18054855
- PMCID: PMC2266612
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.11.008
Inhibition and brain work
Abstract
The major part of the brain's energy budget ( approximately 60%-80%) is devoted to its communication activities. While inhibition is critical to brain function, relatively little attention has been paid to its metabolic costs. Understanding how inhibitory interneurons contribute to brain energy consumption (brain work) is not only of interest in understanding a fundamental aspect of brain function but also in understanding functional brain imaging techniques which rely on measurements related to blood flow and metabolism. Herein we examine issues relevant to an assessment of the work performed by inhibitory interneurons in the service of brain function.
Figures
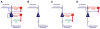


References
-
- Ames A., III CNS energy metabolism as related to function. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2000;34:42–68. - PubMed
-
- Attwell D, Laughlin SB. An energy budget for signaling in the grey matter of the brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2001;21:1133–1145. - PubMed
-
- Attwell D, Gibb A. Neuroenergetics and the kinetic design of excitatory synapses. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:841–849. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

