Dally regulates Dpp morphogen gradient formation by stabilizing Dpp on the cell surface
- PMID: 18054902
- PMCID: PMC2238337
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.10.035
Dally regulates Dpp morphogen gradient formation by stabilizing Dpp on the cell surface
Abstract
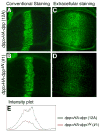
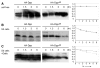
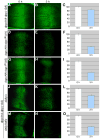
Decapentaplegic (Dpp), a Drosophila homologue of bone morphogenetic proteins, acts as a morphogen to regulate patterning along the anterior-posterior axis of the developing wing. Previous studies showed that Dally, a heparan sulfate proteoglycan, regulates both the distribution of Dpp morphogen and cellular responses to Dpp. However, the molecular mechanism by which Dally affects the Dpp morphogen gradient remains to be elucidated. Here, we characterized activity, stability, and gradient formation of a truncated form of Dpp (Dpp(Delta N)), which lacks a short domain at the N-terminus essential for its interaction with Dally. Dpp(Delta N) shows the same signaling activity and protein stability as wild-type Dpp in vitro but has a shorter half-life in vivo, suggesting that Dally stabilizes Dpp in the extracellular matrix. Furthermore, genetic interaction experiments revealed that Dally antagonizes the effect of Thickveins (Tkv; a Dpp type I receptor) on Dpp signaling. Given that Tkv can downregulate Dpp signaling by receptor-mediated endocytosis of Dpp, the ability of dally to antagonize tkv suggests that Dally inhibits this process. Based on these observations, we propose a model in which Dally regulates Dpp distribution and signaling by disrupting receptor-mediated internalization and degradation of the Dpp-receptor complex.
Figures


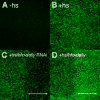
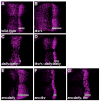
References
-
- Belenkaya TY, Han C, Yan D, Opoka RJ, Khodoun M, Liu H, Lin X. Drosophila Dpp morphogen movement is independent of dynamin-mediated endocytosis but regulated by the glypican members of heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Cell. 2004;119:231–44. - PubMed
-
- Bhanot P, Brink M, Samos CH, Hsieh JC, Wang Y, Macke JP, Andrew D, Nathans J, Nusse R. A new member of the frizzled family from Drosophila functions as a Wingless receptor. Nature. 1996;382:225–30. - PubMed
-
- Brand AH, Perrimon N. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development. 1993;118:401–15. - PubMed
-
- Cherbas L, Moss R, Cherbas P. Transformation techniques for Drosophila cell lines. Methods Cell Biol. 1994;44:161–79. - PubMed
-
- Dubois L, Lecourtois M, Alexandre C, Hirst E, Vincent JP. Regulated endocytic routing modulates wingless signaling in Drosophila embryos. Cell. 2001;105:613–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

