UV-B signaling pathways with different fluence-rate response profiles are distinguished in mature Arabidopsis leaf tissue by requirement for UVR8, HY5, and HYH
- PMID: 18055587
- PMCID: PMC2245850
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.107.108456
UV-B signaling pathways with different fluence-rate response profiles are distinguished in mature Arabidopsis leaf tissue by requirement for UVR8, HY5, and HYH
Abstract
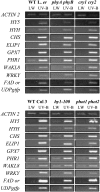
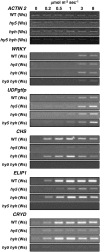
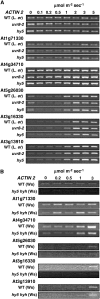
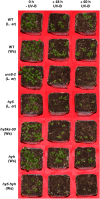
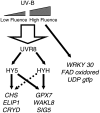
UV-B signaling is an important but poorly understood aspect of light responsiveness in plants. Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) UV RESISTANCE LOCUS8 (UVR8) is a recently identified UV-B-specific signaling component that regulates UV-protective responses. Using the uvr8 mutant, we defined genetically distinct UVR8-dependent and UVR8-independent pathways that stimulate different sets of genes in mature Arabidopsis leaf tissue. Both pathways operate at 1 micromol m(-2) s(-1) UV-B and above, but the UVR8-dependent pathway is able to stimulate UV-protective genes even in response to 0.1 micromol m(-2) s(-1) UV-B. Both pathways function in mutants lacking phytochromes, cryptochromes, or phototropins. Genes encoding the ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL5 (HY5) and HY5 HOMOLOG (HYH) transcription factors are induced at low UV-B fluence rates (0.1 micromol m(-2) s(-1)). Experiments with hy5 and hyh mutants reveal that both these factors mediate responses of the UVR8-dependent pathway, acting with partial or complete redundancy to stimulate expression of particular genes. Furthermore, evidence is presented that all UVR8 pathway genes are likely to be regulated by HY5/HYH and that these transcription factors do not mediate UV-B responses independent of UVR8. Finally, we highlight the functions of HY5 and HYH in UV protection and show that HY5 plays the more critical role. This research provides evidence that, in UV-B signaling, UVR8, HY5, and HYH act together in a photoregulatory pathway and demonstrates a new role for HYH in UV-B responses.
Figures


References
-
- A-H-Mackerness S (2000) Plant responses to ultraviolet-B (UV-B: 280-320 nm) stress: What are the key regulators? Invited review. Plant Growth Regul 32 27–39
-
- A-H-Mackerness S, John CF, Jordan B, Thomas B (2001) Early signaling components in ultraviolet-B responses: distinct roles for different reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide. FEBS Lett 489 237–242 - PubMed
-
- Ahmad M, Cashmore AR (1993) HY4 gene of A. thaliana encodes a protein with characteristics of a blue-light photoreceptor. Nature 366 162–166 - PubMed
-
- Breitling R, Armengaud P, Amtmann A, Herzyk P (2004) Rank products: a simple, yet powerful, new method to detect differentially regulated genes in replicated microarray experiments. FEBS Lett 573 83–92 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

