The effect of optical zone decentration on lower- and higher-order aberrations after photorefractive keratectomy in a cat model
- PMID: 18055835
- PMCID: PMC2815350
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.07-0661
The effect of optical zone decentration on lower- and higher-order aberrations after photorefractive keratectomy in a cat model
Abstract
Purpose: To simulate the effects of decentration on lower- and higher-order aberrations (LOAs and HOAs) and optical quality, by using measured wavefront error (WFE) data from a cat photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) model.
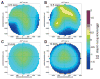
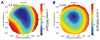
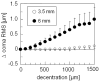
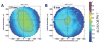
Methods: WFE differences were obtained from five cats' eyes 19 +/-7 weeks after spherical myopic PRK for -6 D (three eyes) and -10 D (two eyes). Ablation-centered WFEs were computed for a 9.0 mm pupil. A computer model was used to simulate decentration of a 6-mm subaperture in 100-microm steps over a circular area of 3000 microm diameter, relative to the measured WFE difference. Changes in LOA, HOA, and image quality (visual Strehl ratio based on the optical transfer function; VSOTF) were computed for simulated decentrations over 3.5 and 6.0 mm.
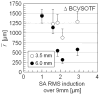
Results: Decentration resulted in undercorrection of sphere and induction of astigmatism; among the HOAs, decentration mainly induced coma. Decentration effects were distributed asymmetrically. Decentrations >1000 microm led to an undercorrection of sphere and cylinder of >0.5 D. Computational simulation of LOA/HOA interaction did not alter threshold values. For image quality (decrease of best-corrected VSOTF by >0.2 log units), the corresponding thresholds were lower. The amount of spherical aberration induced by the centered treatment significantly influenced the decentration tolerance of LOAs and log best corrected VSOTF.
Conclusions: Modeling decentration with real WFE changes showed irregularities of decentration effects for rotationally symmetric treatments. The main aberrations induced by decentration were defocus, astigmatism, and coma. Treatments that induced more spherical aberration were less tolerant of decentration.
Figures
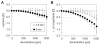
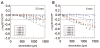
Similar articles
-
Contribution of optical zone decentration and pupil dilation on the change of optical quality after myopic photorefractive keratectomy in a cat model.J Refract Surg. 2010 Mar;26(3):183-90. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20100224-04. Epub 2010 Mar 11. J Refract Surg. 2010. PMID: 20229950 Free PMC article.
-
Zyoptix wavefront-guided versus standard photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) in low and moderate myopia: randomized controlled 6-month study.Eur J Ophthalmol. 2006 Mar-Apr;16(2):219-28. doi: 10.1177/112067210601600205. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2006. PMID: 16703538 Clinical Trial.
-
Optical performance of the cornea six years following photorefractive keratectomy for myopia.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Feb 11;52(2):846-57. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-5905. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21051709
-
Long-term corneal wavefront aberration variations after photorefractive keratectomy for myopia and myopic astigmatism.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011 Sep;37(9):1655-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2011.03.046. Epub 2011 Jul 22. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011. PMID: 21782383
-
Wavefront excimer laser refractive surgery for adults with refractive errors.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Dec 18;12(12):CD012687. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012687.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33336797 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
First demonstration of ocular refractive change using blue-IRIS in live cats.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Jul 1;55(7):4603-12. doi: 10.1167/iovs.14-14373. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014. PMID: 24985471 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in the TGF-{beta}1-induced profibrotic response of anterior and posterior corneal keratocytes in vitro.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010 Apr;51(4):1935-42. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-3823. Epub 2009 Nov 11. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010. PMID: 19907023 Free PMC article.
-
The SCHWIND AMARIS Total-Tech Laser as An All-Rounder in Refractive Surgery.Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2009 Jan;16(1):46-53. doi: 10.4103/0974-9233.48868. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2009. PMID: 20142960 Free PMC article.
-
[Application of wavefront analysis in clinical and scientific settings. From irregular astigmatism to aberrations of a higher order--Part II: examples].Ophthalmologe. 2007 Nov;104(11):991-1006; quiz 1007-8. doi: 10.1007/s00347-007-1648-0. Ophthalmologe. 2007. PMID: 18030477 Review. German.
-
Comparative study of wave-front aberration and corneal Asphericity after SMILE and LASEK for myopia: a short and long term study.BMC Ophthalmol. 2019 Mar 20;19(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12886-019-1084-3. BMC Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 30894159 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mrochen M, Kaemmerer M, Mierdel P, Seiler T. Increased higher-order optical aberrations after laser refractive surgery: a problem of subclinical decentration. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001;27:362–369. - PubMed
-
- Mihashi T. Higher-order wavefront aberrations induced by small ablation area and sub-clinical decentration in simulated corneal refractive surgery using a perturbed schematic eye model. Semin Ophthalmol. 2003;18:41–47. - PubMed
-
- Bueeler M, Mrochen M, Seiler T. Maximum permissible lateral decentration in aberration-sensing and wavefront-guided corneal ablation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003;29:257–263. - PubMed
-
- Bueeler M, Mrochen M, Seiler T. Maximum permissible torsional misalignment in aberration-sensing and wavefront-guided corneal ablation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004;30:17–25. - PubMed
-
- Mrochen M, Eldine MS, Kaemmerer M, Seiler T, Hutz W. Improvement in photorefractive corneal laser surgery results using an active eye-tracking system. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001;27:1000–1006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

