Computational and experimental identification of novel human imprinted genes
- PMID: 18055845
- PMCID: PMC2099581
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.6584707
Computational and experimental identification of novel human imprinted genes
Abstract
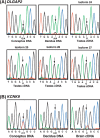
Imprinted genes are essential in embryonic development, and imprinting dysregulation contributes to human disease. We report two new human imprinted genes: KCNK9 is predominantly expressed in the brain, is a known oncogene, and may be involved in bipolar disorder and epilepsy, while DLGAP2 is a candidate bladder cancer tumor suppressor. Both genes lie on chromosome 8, not previously suspected to contain imprinted genes. We identified these genes, along with 154 others, based on the predictions of multiple classification algorithms using DNA sequence characteristics as features. Our findings demonstrate that DNA sequence characteristics, including recombination hot spots, are sufficient to accurately predict the imprinting status of individual genes in the human genome.
Figures
References
-
- Allen E., Horvath S., Tong F., Kraft P., Spiteri E., Riggs A.D., Marahrens Y., Horvath S., Tong F., Kraft P., Spiteri E., Riggs A.D., Marahrens Y., Tong F., Kraft P., Spiteri E., Riggs A.D., Marahrens Y., Kraft P., Spiteri E., Riggs A.D., Marahrens Y., Spiteri E., Riggs A.D., Marahrens Y., Riggs A.D., Marahrens Y., Marahrens Y. High concentrations of long interspersed nuclear element sequence distinguish monoallelically expressed genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2003;100:9940–9945. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arsenian S., Weinhold B., Oelgeschlager M., Ruther U., Nordheim A., Weinhold B., Oelgeschlager M., Ruther U., Nordheim A., Oelgeschlager M., Ruther U., Nordheim A., Ruther U., Nordheim A., Nordheim A. Serum response factor is essential for mesoderm formation during mouse embryogenesis. EMBO J. 1998;17:6289–6299. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bantignies F., Cavalli G., Cavalli G. Cellular memory and dynamic regulation of polycomb group proteins. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2006;18:275–283. - PubMed
-
- Barlow D.P. Methylation and imprinting: from host defense to gene regulation? Science. 1993;260:309–310. - PubMed
-
- Barlow D.P., Stoger R., Herrmann B.G., Saito K., Schweifer N., Stoger R., Herrmann B.G., Saito K., Schweifer N., Herrmann B.G., Saito K., Schweifer N., Saito K., Schweifer N., Schweifer N. The mouse insulin-like growth factor type-2 receptor is imprinted and closely linked to the Tme locus. Nature. 1991;349:84–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
