Prolonged (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate-driven antimicrobial and cytotoxic responses of pulmonary and systemic Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells in macaques
- PMID: 18056373
- PMCID: PMC2865221
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.12.8287
Prolonged (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate-driven antimicrobial and cytotoxic responses of pulmonary and systemic Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells in macaques
Abstract
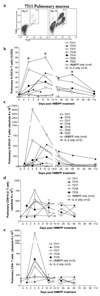
Although phosphoantigen-specific Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells appear to play a role in antimicrobial and anticancer immunity, mucosal immune responses and effector functions of these gammadelta T cells during infection or phospholigand treatment remain poorly characterized. In this study, we demonstrate that the microbial phosphoantigen (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate (HMBPP) plus IL-2 treatment of macaques induced a prolonged major expansion of circulating Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells that expressed CD8 and produced cytotoxic perforin during their peak expansion. Interestingly, HMBPP-activated Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells underwent an extraordinary pulmonary accumulation, which lasted for 3-4 mo, although circulating Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells had returned to baseline levels weeks prior. The Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells that accumulated in the lung following HMBPP/IL-2 cotreatment displayed an effector memory phenotype, as follows: CCR5+CCR7-CD45RA-CD27+ and were able to re-recognize phosphoantigen and produce copious amounts of IFN-gamma up to 15 wk after treatment. Furthermore, the capacity of massively expanded Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells to produce cytokines in vivo coincided with an increase in numbers of CD4+ and CD8+ alphabeta T cells after HMBPP/IL-2 cotreatment as well as substantial perforin expression by CD3+Vgamma2- T cells. Thus, the prolonged HMBPP-driven antimicrobial and cytotoxic responses of pulmonary and systemic Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells may confer immunotherapeutics against infectious diseases and cancers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Poccia F, Battistini L, Cipriani B, Mancino G, Martini F, Gougeon ML, Colizzi V. Phosphoantigen-reactive Vγ9Vδ2 T lymphocytes suppress in vitro human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by cell-released antiviral factors including CC chemokines. J. Infect. Dis. 1999;180:858–861. - PubMed
-
- Dieli F, Troye-Blomberg M, Ivanyi J, Fournie JJ, Bonneville M, Peyrat MA, Sireci G, Salerno A. Vγ9/Vδ2 T lymphocytes reduce the viability of intracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000;30:1512–1519. - PubMed
-
- Ottones F, Dornand J, Naroeni A, Liautard JP, Favero J. Vγ9Vδ2 T cells impair intracellular multiplication of Brucella suis in autologous monocytes through soluble factor release and contact-dependent cytotoxic effect. J. Immunol. 2000;165:7133–7139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

