Rap1a null mice have altered myeloid cell functions suggesting distinct roles for the closely related Rap1a and 1b proteins
- PMID: 18056377
- PMCID: PMC2722108
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.12.8322
Rap1a null mice have altered myeloid cell functions suggesting distinct roles for the closely related Rap1a and 1b proteins
Erratum in
- J Immunol. 2008 Mar 1;180(5):3612. Munugulavadla, Veerendra [corrected to Munugalavadla, Veerendra]
Abstract
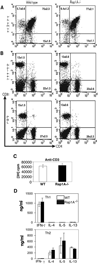
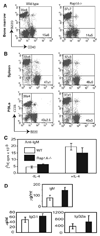
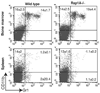
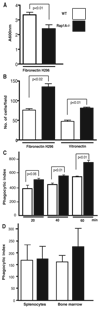
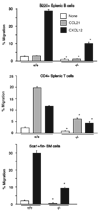
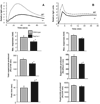
The Ras-related GTPases Rap1a and 1b have been implicated in multiple biological events including cell adhesion, free radical production, and cancer. To gain a better understanding of Rap1 function in mammalian physiology, we deleted the Rap1a gene. Although loss of Rap1a expression did not initially affect mouse size or viability, upon backcross into C57BL/6J mice some Rap1a-/- embryos died in utero. T cell, B cell, or myeloid cell development was not disrupted in Rap1a-/- mice. However, macrophages from Rap1a null mice exhibited increased haptotaxis on fibronectin and vitronectin matrices that correlated with decreased adhesion. Chemotaxis of lymphoid and myeloid cells in response to CXCL12 or CCL21 was significantly reduced. In contrast, an increase in FcR-mediated phagocytosis was observed. Because Rap1a was previously copurified with the human neutrophil NADPH oxidase, we addressed whether GTPase loss affected superoxide production. Neutrophils from Rap1a-/- mice had reduced fMLP-stimulated superoxide production as well as a weaker initial response to phorbol ester. These results suggest that, despite 95% amino acid sequence identity, similar intracellular distribution, and broad tissue distribution, Rap1a and 1b are not functionally redundant but rather differentially regulate certain cellular events.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures
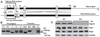
References
-
- Takai Y, Sasaki T, Matozaki T. Small GTP-binding proteins. Physiol. Rev. 2001;81:153–208. - PubMed
-
- Pizon V, Chardin P, Lerosey I, Olofsson B, Tavitian A. Human cDNAs rap1 and rap2 homologous to the Drosophila gene Dras3 encode proteins closely related to ras in the 'effector' region. Oncogene. 1988;3:201–204. - PubMed
-
- Bokoch GM, Parkos CA. Identification of novel GTP-binding proteins in the human neutrophil. FEBS Lett. 1988;227:66–70. - PubMed
-
- Kawata M, Matsui Y, Kondo J, Hishida T, Teranishi Y, Takai Y. A novel small molecular weight GTP-binding protein with the same putative effector domain as the ras proteins in bovine brain membranes. Purification, determination of primary structure, and characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1988;263:18965–18971. - PubMed
-
- Quinn MT, Parkos CA, Walker L, Orkin SH, Dinauer MC, Jesaitis AJ. Association of a Ras-related protein with cytochrome b of human neutrophils. Nature. 1989;342:198–200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

