Hepatic IGFBP1 is a prosurvival factor that binds to BAK, protects the liver from apoptosis, and antagonizes the proapoptotic actions of p53 at mitochondria
- PMID: 18056423
- PMCID: PMC2081976
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1567107
Hepatic IGFBP1 is a prosurvival factor that binds to BAK, protects the liver from apoptosis, and antagonizes the proapoptotic actions of p53 at mitochondria
Abstract
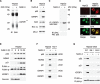
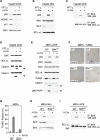
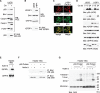
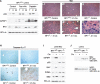
Liver is generally refractory to apoptosis induced by the p53 tumor suppressor protein, but the molecular basis remains poorly understood. Here we show that p53 transcriptional activation leads to enhanced expression of hepatic IGFBP1 (insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1). Exhibiting a previously unanticipated role, a portion of intracellular IGFBP1 protein localizes to mitochondria where it binds to the proapoptotic protein BAK and hinders BAK activation and apoptosis induction. Interestingly, in many cells and tissues p53 also has a direct apoptotic function at mitochondria that includes BAK binding and activation. When IGFBP1 is in a complex with BAK, formation of a proapoptotic p53/BAK complex and apoptosis induction are impaired, both in cultured cells and in liver. In contrast, livers of IGFBP1-deficient mice exhibit spontaneous apoptosis that is accompanied by p53 mitochondrial accumulation and evidence of BAK oligomerization. These data support the importance of BAK as a mediator of p53's mitochondrial function. The results also identify IGFBP1 as a negative regulator of the BAK-dependent pathway of apoptosis, whose expression integrates the transcriptional and mitochondrial functions of the p53 tumor suppressor protein.
Figures


References
-
- Amundson S., Myers T., Scudiero D., Kitada S., Reed J., Fornace A., Myers T., Scudiero D., Kitada S., Reed J., Fornace A., Scudiero D., Kitada S., Reed J., Fornace A., Kitada S., Reed J., Fornace A., Reed J., Fornace A., Fornace A. An informatics approach identifying markers of chemosensitivity in human cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2000;60:6101–6110. - PubMed
-
- Arima Y., Nitta M., Kuninaka S., Zhang D., Fujiwara T., Taya Y., Nakao M., Saya H., Nitta M., Kuninaka S., Zhang D., Fujiwara T., Taya Y., Nakao M., Saya H., Kuninaka S., Zhang D., Fujiwara T., Taya Y., Nakao M., Saya H., Zhang D., Fujiwara T., Taya Y., Nakao M., Saya H., Fujiwara T., Taya Y., Nakao M., Saya H., Taya Y., Nakao M., Saya H., Nakao M., Saya H., Saya H. Transcriptional blockade induces p53-dependent apoptosis associated with translocation of p53 to mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:19166–19176. - PubMed
-
- Bensaad K., Tsuruta A., Selak M., Vidal M., Nakano K., Bartrons R., Gottlieb E., Vousden K., Tsuruta A., Selak M., Vidal M., Nakano K., Bartrons R., Gottlieb E., Vousden K., Selak M., Vidal M., Nakano K., Bartrons R., Gottlieb E., Vousden K., Vidal M., Nakano K., Bartrons R., Gottlieb E., Vousden K., Nakano K., Bartrons R., Gottlieb E., Vousden K., Bartrons R., Gottlieb E., Vousden K., Gottlieb E., Vousden K., Vousden K. TIGAR, a p53-inducible regulator of glycolysis and apoptosis. Cell. 2006;126:107–120. - PubMed
-
- Brooks C., Wei Q., Feng L., Dong G., Tao Y., Mei L., Xie Z., Dong Z., Wei Q., Feng L., Dong G., Tao Y., Mei L., Xie Z., Dong Z., Feng L., Dong G., Tao Y., Mei L., Xie Z., Dong Z., Dong G., Tao Y., Mei L., Xie Z., Dong Z., Tao Y., Mei L., Xie Z., Dong Z., Mei L., Xie Z., Dong Z., Xie Z., Dong Z., Dong Z. Bak regulates mitochondrial morphology and pathology during apoptosis by interacting with mitofusins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2007;104:11649–11654. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
