Structure, inhibitor, and regulatory mechanism of Lyp, a lymphoid-specific tyrosine phosphatase implicated in autoimmune diseases
- PMID: 18056643
- PMCID: PMC2148373
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0706233104
Structure, inhibitor, and regulatory mechanism of Lyp, a lymphoid-specific tyrosine phosphatase implicated in autoimmune diseases
Abstract
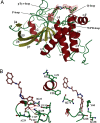
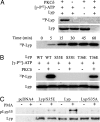
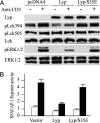
The lymphoid-specific tyrosine phosphatase (Lyp) has generated enormous interest because a single-nucleotide polymorphism in the gene (PTPN22) encoding Lyp produces a gain-of-function mutant phosphatase that is associated with several autoimmune diseases, including type I diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, Graves disease, and systemic lupus erythematosus. Thus, Lyp represents a potential target for a broad spectrum of autoimmune disorders. Unfortunately, no Lyp inhibitor has been reported. In addition, little is known about the structure and biochemical mechanism that directly regulates Lyp function. Here, we report the identification of a bidentate salicylic acid-based Lyp inhibitor I-C11 with excellent cellular efficacy. Structural and mutational analyses indicate that the inhibitor binds both the active site and a nearby peripheral site unique to Lyp, thereby furnishing a solid foundation upon which inhibitors with therapeutic potency and selectivity can be developed. Moreover, a comparison of the apo- and inhibitor-bound Lyp structures reveals that the Lyp-specific region S(35)TKYKADK(42), which harbors a PKC phosphorylation site, could adopt either a loop or helical conformation. We show that Lyp is phosphorylated exclusively at Ser-35 by PKC both in vitro and in vivo. We provide evidence that the status of Ser-35 phosphorylation may dictate the conformational state of the insert region and thus Lyp substrate recognition. We demonstrate that Ser-35 phosphorylation impairs Lyp's ability to inactivate the Src family kinases and down-regulate T cell receptor signaling. Our data establish a mechanism by which PKC could attenuate the cellular function of Lyp, thereby augmenting T cell activation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification and structure-function analyses of an allosteric inhibitor of the tyrosine phosphatase PTPN22.J Biol Chem. 2019 May 24;294(21):8653-8663. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.007129. Epub 2019 Apr 12. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30979725 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphoid-specific tyrosine phosphatase (Lyp): a potential drug target for treatment of autoimmune diseases.Curr Drug Targets. 2014 Mar;15(3):335-46. doi: 10.2174/13894501113146660236. Curr Drug Targets. 2014. PMID: 24188455 Review.
-
Inhibition of lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase by benzofuran salicylic acids.J Med Chem. 2011 Jan 27;54(2):562-71. doi: 10.1021/jm101004d. Epub 2010 Dec 29. J Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21190368 Free PMC article.
-
Target-specific control of lymphoid-specific protein tyrosine phosphatase (Lyp) activity.Bioorg Med Chem. 2010 Jul 15;18(14):4884-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2010.06.022. Epub 2010 Jun 12. Bioorg Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20594861 Free PMC article.
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPN22 in human autoimmunity.Autoimmunity. 2007 Sep;40(6):453-61. doi: 10.1080/08916930701464897. Autoimmunity. 2007. PMID: 17729039 Review.
Cited by
-
The rise and fall of anandamide: processes that control synthesis, degradation, and storage.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Jul;476(7):2753-2775. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04121-5. Epub 2021 Mar 13. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33713246 Review.
-
The role for protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 22 in regulating intestinal homeostasis.United European Gastroenterol J. 2016 Jun;4(3):325-32. doi: 10.1177/2050640615600115. Epub 2015 Aug 6. United European Gastroenterol J. 2016. PMID: 27403297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CuAAC click chemistry accelerates the discovery of novel chemical scaffolds as promising protein tyrosine phosphatases inhibitors.Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(15):2399-405. doi: 10.2174/092986712800269245. Curr Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22455590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PTPN22: structure, function, and developments in inhibitor discovery with applications for immunotherapy.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2022 Aug;17(8):825-837. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2022.2084607. Epub 2022 Jun 7. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2022. PMID: 35637605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and structure-function analyses of an allosteric inhibitor of the tyrosine phosphatase PTPN22.J Biol Chem. 2019 May 24;294(21):8653-8663. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.007129. Epub 2019 Apr 12. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30979725 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mustelin T, Abraham RT, Rudd CE, Alonso A, Merlo JJ. Front Biosci. 2002;7:d918–d969. - PubMed
-
- Palacios EH, Weiss A. Oncogene. 2004;23:7990–8000. - PubMed
-
- Bottini N, Musumeci L, Alonso A, Rahmouni S, Nika K, Rostamkhani M, MacMurray J, Meloni GF, Lucarelli P, Pellecchia M, et al. Nat Genet. 2004;36:337–338. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

