Chronic late-gestation hypoglycemia upregulates hepatic PEPCK associated with increased PGC1alpha mRNA and phosphorylated CREB in fetal sheep
- PMID: 18056789
- PMCID: PMC3857025
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00639.2007
Chronic late-gestation hypoglycemia upregulates hepatic PEPCK associated with increased PGC1alpha mRNA and phosphorylated CREB in fetal sheep
Abstract
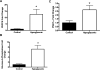
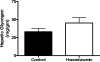
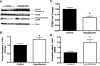
Hepatic glucose production is normally activated at birth but has been observed in response to experimental hypoglycemia in fetal sheep. The cellular basis for this process remains unknown. We determined the impact of 2 wk of fetal hypoglycemia during late gestation on enzymes responsible for hepatic gluconeogenesis, focusing on the insulin-signaling pathway, transcription factors, and coactivators that regulate gluconeogenesis. Hepatic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and glucose-6-phosphatase mRNA increased 12-fold and 7-fold, respectively, following chronic hypoglycemia with no change in hepatic glycogen. Chronic hypoglycemia decreased fetal plasma insulin with no change in glucagon but increased plasma cortisol 3.5-fold. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1alpha mRNA and phosphorylation of cAMP response element binding protein at Ser(133) were both increased, with no change in Akt, forkhead transcription factor FoxO1, hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha, or CCAAT enhancer binding protein-beta. These results demonstrate that chronic fetal hypoglycemia triggers signals that can activate gluconeogenesis in the fetal liver.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene expression and steatosis during hepatitis C virus subgenome replication: role of nonstructural component 5A and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β.J Biol Chem. 2012 Oct 26;287(44):37340-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.384743. Epub 2012 Sep 6. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22955269 Free PMC article.
-
An active part of Artemisia sacrorum Ledeb. suppresses gluconeogenesis through AMPK mediated GSK3β and CREB phosphorylation in human HepG2 cells.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2011;75(6):1079-84. doi: 10.1271/bbb.100881. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21670525
-
The SMILE transcriptional corepressor inhibits cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB)-mediated transactivation of gluconeogenic genes.J Biol Chem. 2018 Aug 24;293(34):13125-13133. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002196. Epub 2018 Jun 27. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29950523 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factors and coactivators controlling nutrient and hormonal regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012 Jan;44(1):33-45. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2011.10.001. Epub 2011 Oct 8. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22004992 Review.
-
Novel concepts in insulin regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2003 Oct;285(4):E685-92. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00253.2003. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2003. PMID: 12959935 Review.
Cited by
-
Coordinated changes in hepatic amino acid metabolism and endocrine signals support hepatic glucose production during fetal hypoglycemia.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Feb 15;308(4):E306-14. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00396.2014. Epub 2014 Dec 16. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 25516551 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of chronic hypoglycemia and euglycemic correction on lysine metabolism in fetal sheep.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Apr;296(4):E879-87. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.90832.2008. Epub 2009 Feb 3. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009. PMID: 19190258 Free PMC article.
-
A physiological increase in insulin suppresses gluconeogenic gene activation in fetal sheep with sustained hypoglycemia.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2012 Oct 15;303(8):R861-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00331.2012. Epub 2012 Aug 29. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22933022 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation patterns and gene expression associated with litter size in Berkshire pig placenta.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 7;12(9):e0184539. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184539. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28880934 Free PMC article.
-
Remembering development - epigenetic responses to fetal malnutrition.J Physiol. 2010 May 1;588(Pt 9):1379-80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.189787. J Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20436037 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Barry JS, Davidsen ML, Limesand SW, Galan HL, Friedman JE, Regnault TRH, Hay WW., Jr. Developmental Changes in Ovine Myocardial Glucose Transporters and Insulin Signaling Following Hyperthermia-Induced Intrauterine Fetal Growth Restriction. Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2006;231:566–575. - PubMed
-
- Bossi E, Greenberg RE. Sources of blood glucose in the rat fetus. Pediatr Res. 1972;6:765–772. - PubMed
-
- Boustead JN, Stadelmaier BT, Eeds AM, Wiebe PO, Svitek CA, Oeser JK, O'Brien RM. Hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 alpha mediates the stimulatory effect of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma co-activator-1 alpha (PGC-1 alpha) on glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit gene transcription in H4IIE cells. Biochem J. 2003;369:17–22. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 DK057516/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HD28794/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD028794/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD007186/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD042815/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK048520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK052138/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RR 00069/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK 52138/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000069/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK067393/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 2P30 DK 48520-11/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HD 07186/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- DK 67393/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HD 48215/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK 57516/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

