BCL-2 dependence and ABT-737 sensitivity in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 18056841
- PMCID: PMC2234061
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-06-098012
BCL-2 dependence and ABT-737 sensitivity in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
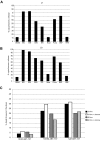
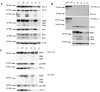
Cancer cells acquire disruptions in normal signal transduction pathways and homeostatic mechanisms that would trigger apoptosis in normal cells. These abnormalities include genomic instability, oncogene activation, and growth factor independent proliferation. Therefore, cancer cells likely require a block in apoptosis in order to survive. Overexpression of the antiapoptotic protein BCL-2 provides a block in apoptosis that is frequently observed in cancer cells. We have developed methods for the detection and analysis of BCL-2 dependence and here apply them to acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). BH3 profiling, a mitochondrial assay that classifies blocks in the intrinsic apoptotic pathway, indicated a dependence on BCL-2 of both ALL cell lines and primary samples. This dependence predicted that BCL-2 would be complexed with select pro-death BH3 family proteins, a prediction confirmed by the isolation of BCL-2 complexes with BIM. Furthermore, the BH3 profiling and protein analysis predicted that ALL cell lines and primary cells would be sensitive to ABT-737 as a single agent. Finally, BH3 profiling and protein studies accurately predicted a relative degree of sensitivity to BCL-2 antagonism in cell lines. The ALL cells studied exhibit BCL-2 dependence, supporting clinical trials of BCL-2 antagonists in ALL as single agents or combination therapies.
Figures
References
-
- Pui CH, Jeha S. New therapeutic strategies for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6:149–165. - PubMed
-
- Thomas DA, Cortes J, Kantarjian HM. New agents in the treatment of acute lymphocytic leukaemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2002;15:771–790. - PubMed
-
- Hahn WC, Weinberg RA. Modelling the molecular circuitry of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:331–341. - PubMed
-
- Green DR, Evan GI. A matter of life and death. Cancer Cell. 2002;1:19–30. - PubMed
-
- Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ. Cell death: critical control points. Cell. 2004;116:205–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

