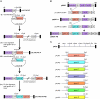
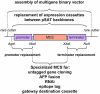
Delivery of multiple transgenes to plant cells
- PMID: 18056862
- PMCID: PMC2151730
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.107.106104
Delivery of multiple transgenes to plant cells
Figures
References
-
- Arnould S, Chames P, Perez C, Lacroix E, Duclert A, Epinat JC, Stricher F, Petit AS, Patin A, Guillier S, et al (2006) Engineering of large numbers of highly specific homing endonucleases that induce recombination on novel DNA targets. J Mol Biol 355 443–458 - PubMed
-
- Becker D, Kemper E, Schell J, Masterson R (1992) New plant binary vectors with selectable markers located proximal to the left T-DNA border. Plant Mol Biol 20 1195–1197 - PubMed
-
- Bohmert K, Balbo I, Kopka J, Mittendorf V, Nawrath C, Poirier Y, Tischendorf G, Trethewey RN, Willmitzer L (2000) Transgenic Arabidopsis plants can accumulate polyhydroxybutyrate to up to 4% of their fresh weight. Planta 211 841–845 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

