Diabetes-related complications, glycemic control, and falls in older adults
- PMID: 18056893
- PMCID: PMC2288549
- DOI: 10.2337/dc07-1152
Diabetes-related complications, glycemic control, and falls in older adults
Erratum in
- Diabetes Care. 2008 May;31(5):1089
Abstract
Objective: Older adults with type 2 diabetes are more likely to fall, but little is known about risk factors for falls in this population. We determined whether diabetes-related complications or treatments are associated with risk of falls in older diabetic adults.
Research design and methods: In the Health, Aging, and Body Composition cohort of well-functioning older adults, participants reported falls in the previous year at annual visits. Odds ratios (ORs) for more frequent falls among 446 diabetic participants whose mean age was 73.6 years, with an average follow-up of 4.9 years, were estimated with continuation ratio models.
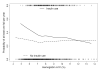
Results: In the first year, 23[corrected]% reported falling; 22, 26, 30[corrected], and 31[corrected]% fell in subsequent years. In adjusted models, reduced peroneal nerve response amplitude (OR 1.50 -95% CI 1.07-2.12], worst quartile versus others); higher cystatin-C, a marker of reduced renal function (1.38 [1.11-1.71], for 1 SD increase); poorer contrast sensitivity (1.41 [0.97-2.04], worst quartile versus others); and low A1C in insulin users (4.36 [1.32-14.46], A1C <or=6 vs. >8%) were associated with risk of falls. In those using oral hypoglycemic medications but not insulin, low A1C was not associated with risk of falls (1.29 [0.65-2.54], A1C <or=6 vs. >8%). Adjustment for physical performance explained some, but not all, of these associations.
Conclusions: In older diabetic adults, reducing diabetes-related complications may prevent falls. Achieving lower A1C levels with oral hypoglycemic medications was not associated with more frequent falls, but, among those using insulin, A1C <or=6% increased risk of falls.
Figures
References
-
- Miller DK, Lui LY, Perry HM, Kaiser FE, Morley JE. Reported and measured physical functioning in older inner-city diabetic African Americans. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1999;54:M230–M236. - PubMed
-
- Hanlon JT, Landerman LR, Fillenbaum GG, Studenski S. Falls in African American and white community-dwelling elderly residents. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2002;57:M473–M478. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz AV, Hillier TA, Sellmeyer DE, Resnick HE, Gregg E, Ensrud KE, Schreiner PJ, Margolis KL, Cauley JA, Nevitt MC, Black DM, Cummings SR. Older women with diabetes have a higher risk of falls: a prospective study. Diabetes Care. 2002;25:1749–1754. - PubMed
-
- Maurer MS, Burcham J, Cheng H. Diabetes mellitus is associated with an increased risk of falls in elderly residents of a long-term care facility. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2005;60:1157–1162. - PubMed

